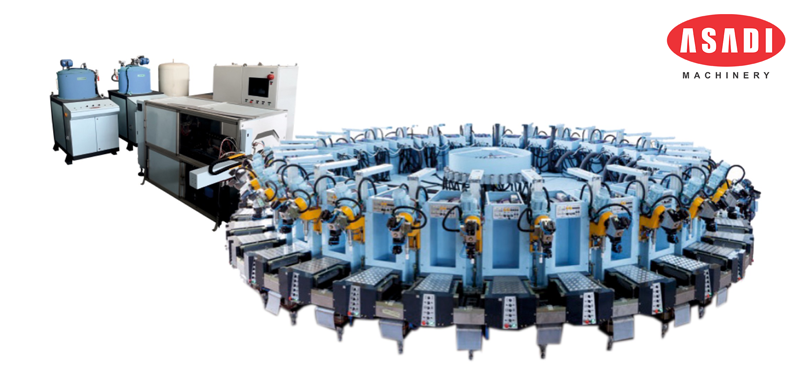
Apparel & Textile Machinery
Apparel and textile machinery encompasses a wide range of equipment used in the production of clothing and textiles.
This machinery plays a crucial role in various stages of the manufacturing process, from spinning fibers into yarn to weaving, knitting, dyeing, printing, and finishing the final product.
1. Spinning Machinery: Spinning machinery is used to convert raw fibers, such as cotton, wool, or synthetic fibers, into yarn. This process involves drawing, twisting, and winding fibers to create yarn of the desired thickness and strength.
2. Weaving Machinery: Weaving machinery is used to interlace two sets of yarns (warp and weft) to create fabric. There are different types of weaving machines, including shuttle looms, rapier looms, air jet looms, and water jet looms, each suited for different types of fabrics and production requirements.
3. Knitting Machinery: Knitting machinery is used to create knitted fabrics by interlocking yarn loops. Knitting machines can produce a variety of fabrics, from simple jersey knits to complex textured patterns.
4. Dyeing and Finishing Machinery: Dyeing machinery is used to apply color to fabric, while finishing machinery is used to improve the appearance, texture, and functionality of the fabric. This includes processes such as bleaching, mercerizing, calendering, and coating.
5. Printing Machinery: Printing machinery is used to apply designs, patterns, or images onto fabric. There are various printing techniques, including screen printing, rotary printing, digital printing, and heat transfer printing.
6. Cutting and Sewing Machinery: Cutting machinery is used to cut fabric into pattern pieces, while sewing machinery is used to stitch these pieces together to create garments. Automated cutting and sewing machines have become increasingly common in mass production facilities, improving efficiency and precision.
7. Embroidery Machinery: Embroidery machinery is used to add decorative stitching to fabric, creating intricate designs or patterns. Computerized embroidery machines allow for precise control and automation of the embroidery process.
8. Textile Testing Equipment: Textile testing equipment is used to assess the quality, performance, and properties of textiles, ensuring they meet industry standards and customer requirements. This includes equipment for measuring tensile strength, colorfastness, fabric thickness, and other parameters.
Overall, apparel and textile machinery plays a vital role in the textile industry, facilitating the production of a wide range of textiles and clothing items efficiently and with high quality. Advances in technology continue to drive innovation in this sector, improving productivity, sustainability, and the quality of finished products.

Apparel and textile machinery is used in the production of a wide range of clothing items, including but not limited to:
1. T-shirts
2. Jeans
3. Dresses
4. Shirts
5. Pants
6. Skirts
7. Jackets
8. Suits
9. Undergarments (e.g., underwear, bras)
10. Sportswear
11. Outerwear (e.g., coats, parkas)
12. Swimwear
13. Sleepwear (e.g., pajamas, nightgowns)
14. Workwear (e.g., uniforms, coveralls)
15. Accessories (e.g., scarves, hats, gloves)
Each of these clothing items requires different manufacturing processes, and apparel and textile machinery is utilized at various stages of production to cut, sew, dye, print, and finish the fabric to create the final garments. Whether it's mass production in large factories or small-scale production in boutique workshops, apparel and textile machinery plays a crucial role in meeting the demands of the global fashion industry.
The advantages of apparel and textile machinery include:
1. Increased Efficiency: Machinery automates many processes in textile production, leading to higher productivity and reduced labor costs. Tasks that would be time-consuming or difficult for humans to perform manually can be completed quickly and accurately by machines.
2. Improved Quality: Machinery allows for precise control over various aspects of production, resulting in consistent quality and fewer defects in the final products. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and fewer returns or rejections due to manufacturing flaws.
3. Cost Savings: While the initial investment in machinery can be significant, over time, it often leads to cost savings through increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and minimized material waste. This can improve the overall profitability of textile manufacturing operations.
4. Faster Turnaround Times: Machinery enables faster production cycles, allowing manufacturers to respond more quickly to changes in market demand or customer preferences. This agility can give companies a competitive edge in the fast-paced fashion industry.
5. Versatility: Modern textile machinery is often designed to handle a wide range of fabrics and production processes. This versatility allows manufacturers to produce diverse product lines and adapt to changing trends or customer requirements with relative ease.
6. Conservation of Resources: Advanced machinery is often more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, automated processes can help minimize material waste and optimize resource utilization, contributing to sustainability goals.
7. Innovation and Customization: Machinery enables manufacturers to experiment with new materials, techniques, and designs, fostering innovation in the textile industry. It also facilitates customization and personalization of products to meet the unique needs and preferences of consumers.
8. Scalability: Textile machinery can be scaled up or down to accommodate changes in production volume, allowing manufacturers to ramp up production during peak seasons or scale back during slower periods without significant disruption to operations.
Overall, apparel and textile machinery offers numerous advantages that contribute to the efficiency, quality, flexibility, and sustainability of textile manufacturing processes.
apparel and textile machinery are suitable for processing both fabrics and leathers, although different types of machinery may be required depending on the material and the specific manufacturing processes involved.
1. Fabrics: Textile machinery is designed to handle a wide variety of fabrics, including natural fibers like cotton, wool, and silk, as well as synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic. Machinery such as spinning frames, weaving looms, knitting machines, dyeing equipment, and finishing machinery are all used in the production of fabric-based garments and textiles.
2. Leather: While leather is not a textile in the traditional sense, it is also processed using specialized machinery in the apparel industry. Leather processing machinery includes equipment for cutting, skiving, splitting, embossing, dyeing, and finishing leather hides to create various leather products such as jackets, shoes, bags, and accessories.

Some machinery is versatile enough to handle both fabrics and leather, while others are specifically designed for one material or the other. For example, cutting and sewing machines may be used for both fabrics and leather, while specialized dyeing or embossing machines may be tailored specifically for leather processing.
In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on developing machinery and processes that can handle a wide range of materials, including both fabrics and leathers, to meet the demand for hybrid and sustainable fashion products. As a result, manufacturers are continually innovating to create more versatile and adaptable machinery that can accommodate various materials and production techniques.

2. Jeans
3. Dresses
4. Shirts
5. Pants
6. Skirts
7. Jackets
8. Suits
9. Undergarments (e.g., underwear, bras)
10. Sportswear
11. Outerwear (e.g., coats, parkas)
12. Swimwear
13. Sleepwear (e.g., pajamas, nightgowns)
14. Workwear (e.g., uniforms, coveralls)
15. Accessories (e.g., scarves, hats, gloves)

FAQs
How has the integration of automation technology transformed the efficiency of apparel and textile machinery?
Automation in apparel and textile machinery boosts efficiency by speeding up processes, ensuring precision, and allowing for continuous operation. It optimizes workflow, improves quality control, and enhances flexibility in production.
What are some key advancements in dyeing and finishing machinery that have improved sustainability in textile manufacturing?
Key advancements include the development of eco-friendly dyeing processes, such as waterless or low-water dyeing techniques, and the use of sustainable finishing methods, like enzymatic or plasma treatments, which reduce chemical usage and environmental impact.
How do manufacturers ensure the versatility of apparel and textile machinery to accommodate a wide range of fabrics and production processes?
Manufacturers design adaptable machinery with adjustable settings and interchangeable components to accommodate various fabrics and production needs efficiently.
In what ways do innovations in cutting-edge embroidery machinery enhance the customization and design capabilities of textile products?
Innovations in cutting-edge embroidery machinery offer precise control over stitching patterns and colors, enabling intricate designs and personalized customization of textile products.





.jpg)