Air condition machinery
Air conditioning machinery plays a pivotal role in maintaining indoor comfort by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality within a defined space. These systems typically consist of various components working together seamlessly to create a controlled environment.
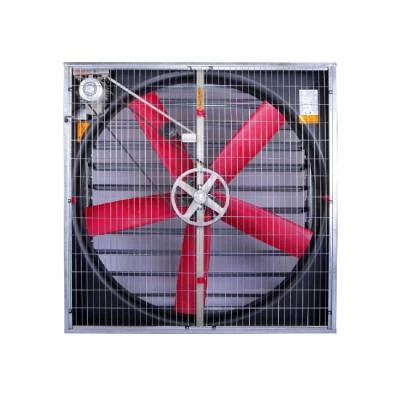
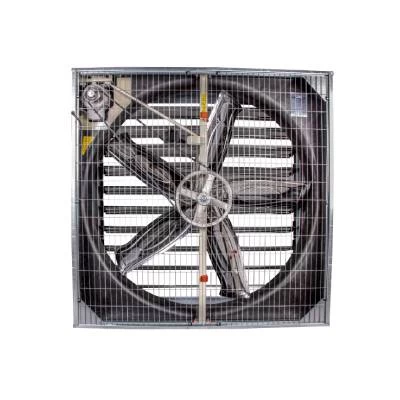
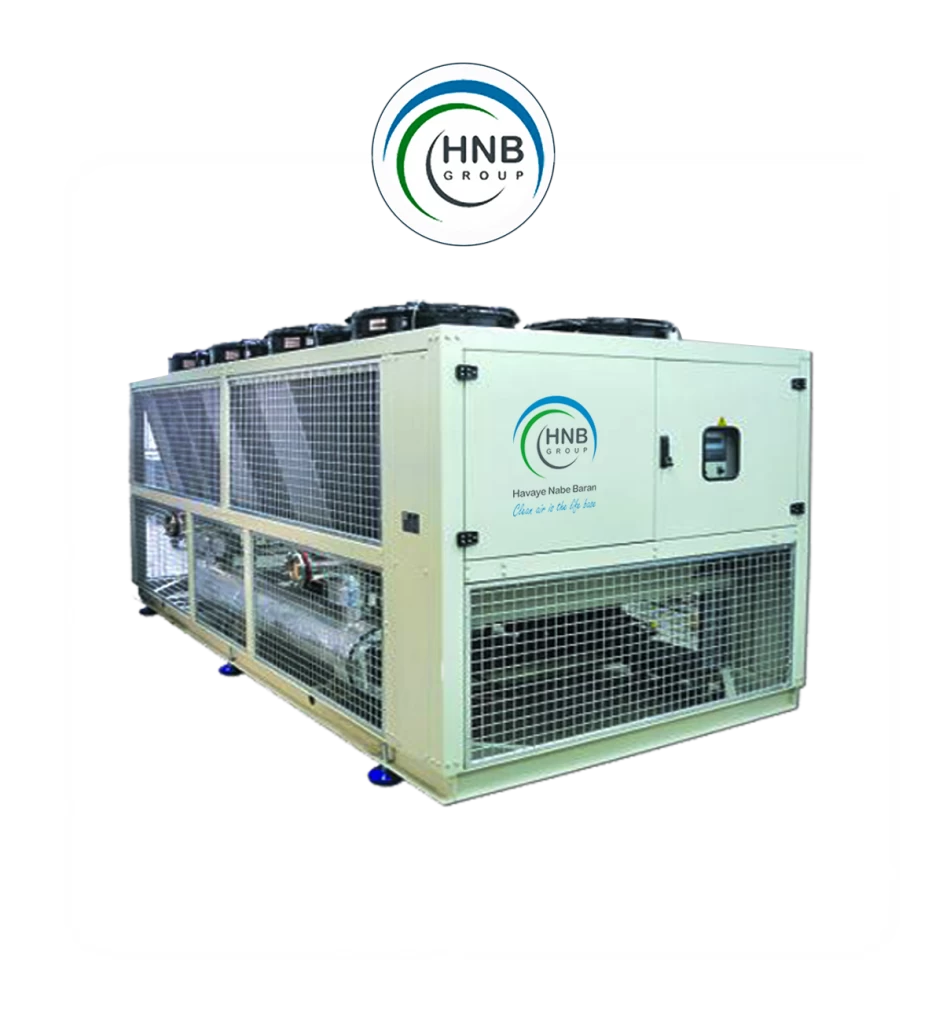
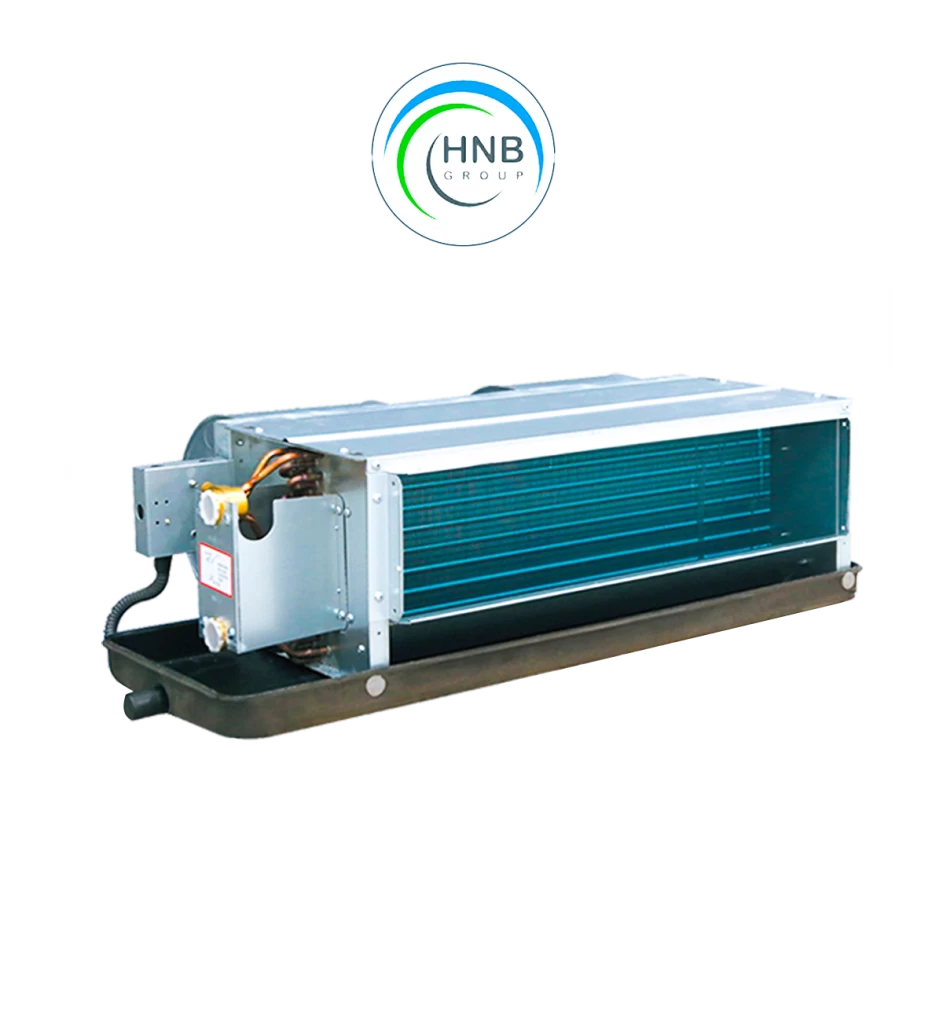
The heart of an air conditioning system is the compressor, responsible for pressurizing and circulating the refrigerant gas. As the refrigerant flows through the system, it undergoes phase changes, absorbing and releasing heat. The evaporator coil facilitates heat absorption from the indoor air, cooling it down, while the condenser coil expels the absorbed heat to the outside. This continuous cycle allows the air conditioner to remove heat from the indoor environment, providing a cooling effect.
To control the temperature accurately, air conditioners utilize a thermostat, which senses the ambient temperature and signals the system to adjust accordingly. Modern air conditioners often come with programmable thermostats, allowing users to set specific temperature preferences for different times of the day.
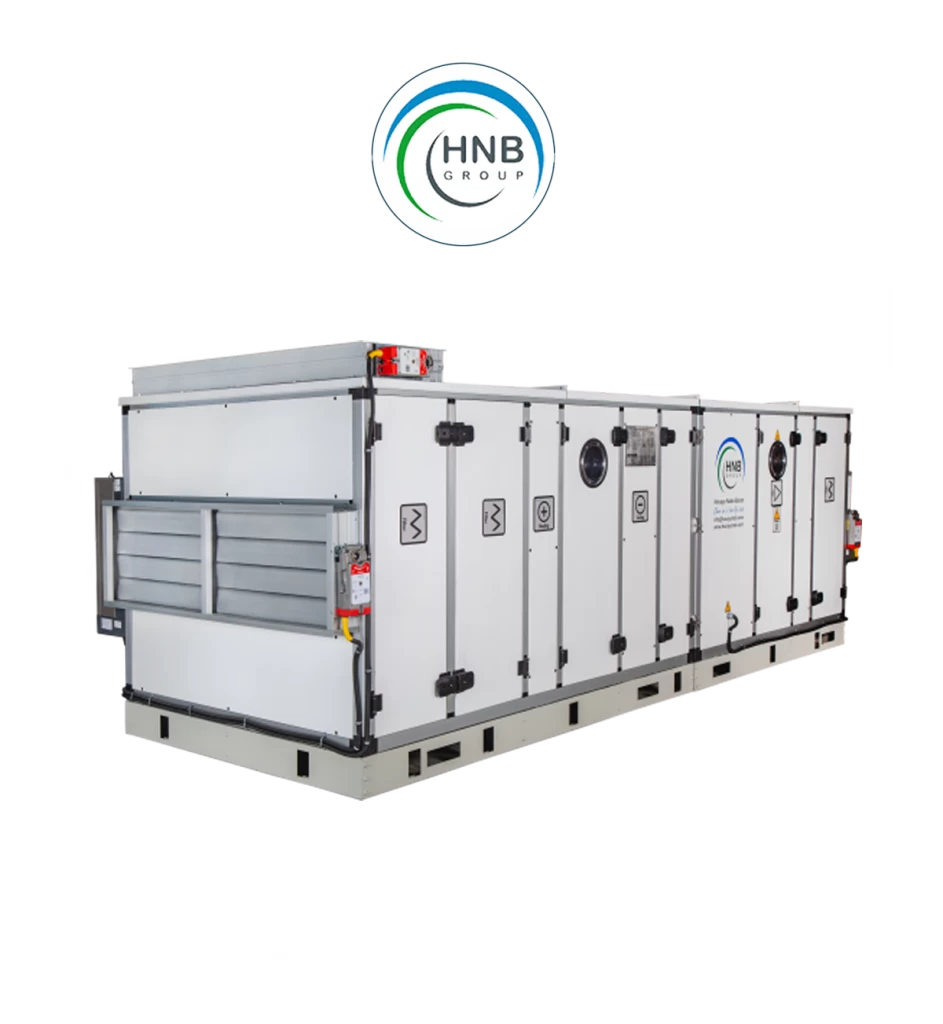
Furthermore, air conditioning systems include air handlers and fans to circulate the conditioned air throughout the space. Filters within the system trap dust, allergens, and other particles, enhancing indoor air quality. Regular maintenance of these filters is crucial for efficient operation and to prevent the buildup of contaminants.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on energy efficiency in air conditioning machinery. Advancements in technology have led to the development of high-efficiency systems that consume less energy while delivering optimal performance. Variable speed compressors and smart controls contribute to better energy management, reducing both environmental impact and operational costs.
The type of refrigerant used in air conditioners is also a critical consideration. Environmental concerns have led to the phasing out of certain refrigerants with high global warming potential. Industry efforts focus on adopting eco-friendly alternatives that minimize the environmental footprint.
In conclusion, air conditioning machinery has evolved significantly to provide effective temperature control and enhance indoor comfort. From compressors to coils, thermostats to filters, each component plays a vital role in creating a conducive indoor environment. Ongoing advancements continue to shape the industry, with a focus on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.

Air conditioning machinery is used in a wide range of settings to create comfortable and controlled environments. Some common applications include:
1. Residential Buildings: Air conditioners are commonly used in homes to maintain a comfortable temperature, especially in regions with extreme climates.
2. Commercial Spaces: Offices, retail stores, and other commercial buildings use air conditioning systems to provide a pleasant working or shopping environment for employees and customers.
3. Industrial Facilities: Large-scale industrial spaces often utilize air conditioning for process control, equipment cooling, and maintaining specific environmental conditions.
4. Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: In healthcare settings, air conditioning is crucial for maintaining sterile environments, controlling humidity, and ensuring the comfort of patients and medical staff.
In essence, air conditioning machinery is utilized in diverse sectors where maintaining specific temperature, humidity, and air quality conditions is essential for comfort, health, productivity, or the preservation of sensitive materials.
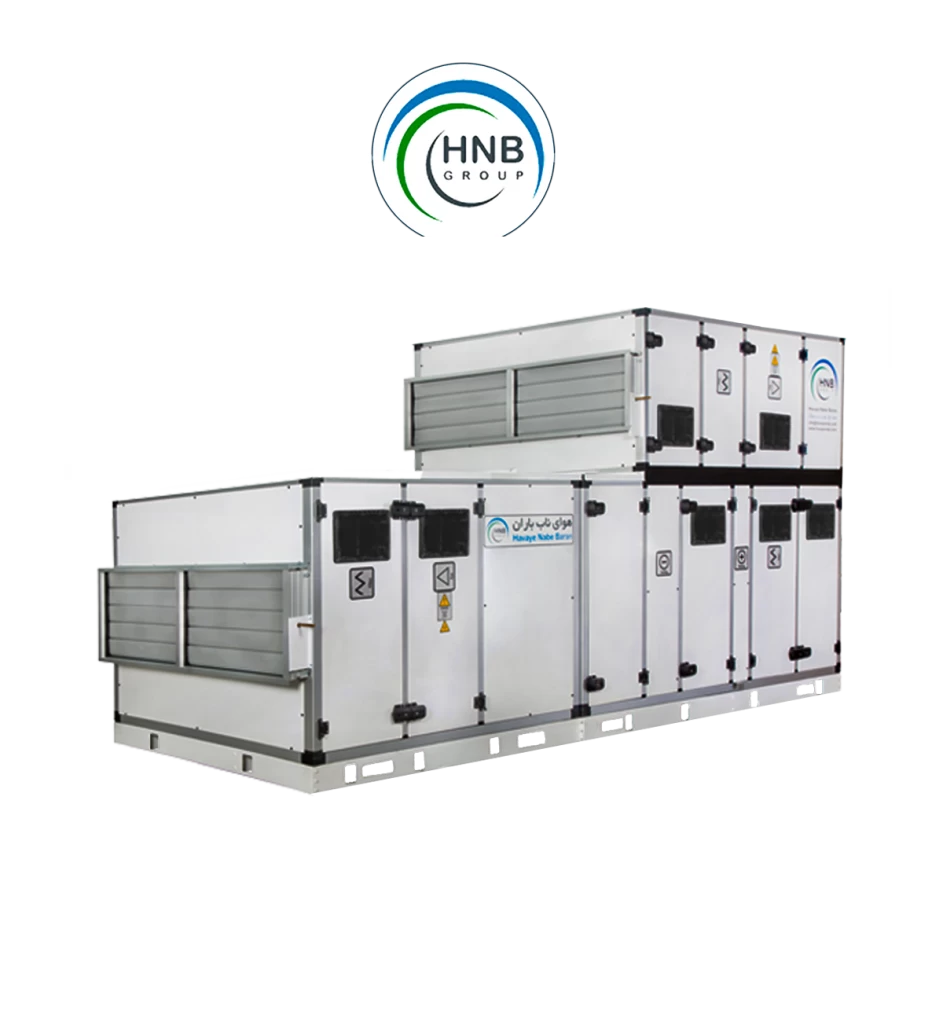
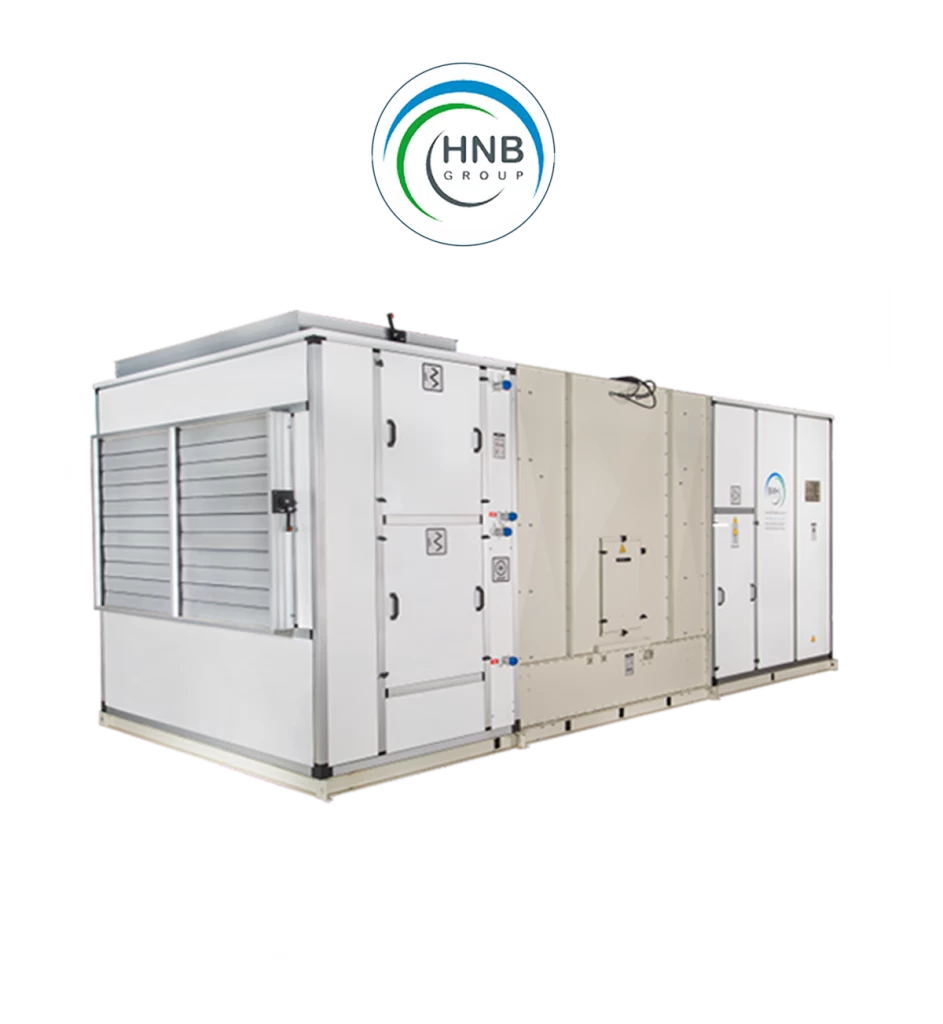
Air conditioning systems encompass a variety of products and components designed to regulate indoor temperature and create comfortable environments. Some key products included in air conditioning systems are:
1. Compressor: The heart of the system, compressors pressurize and circulate the refrigerant, facilitating heat exchange.
2. Evaporator Coil: Located indoors, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, leading to cooling.
3. Condenser Coil: Positioned outdoors, it releases the absorbed heat into the external environment.
4. Refrigerant: The substance circulating in the system, undergoing phase changes to absorb and release heat.
5. Thermostat: A control device that senses the ambient temperature and signals the system to adjust accordingly.
6. Air Handler: Responsible for circulating conditioned air throughout the space.
7. Fans: Assist in the circulation of air and the distribution of conditioned air within the space.
8. Filters: Trap dust, allergens, and particles to improve indoor air quality.
9. Ductwork: Channels that distribute conditioned air throughout the building.
10. Control Panels: Interface for users to set temperature preferences and control system functions.
11. Smart Controls: Advanced systems may include programmable and remote controls for energy-efficient and convenient operation.
12. Ventilation Systems: In some cases, air conditioning systems may be integrated with ventilation systems to bring in fresh outdoor air.
13. Heat Pumps: Some systems function as both heaters and air conditioners, capable of reversing the refrigeration cycle for heating during colder seasons.
These components work synergistically to regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality, providing the desired comfort in various residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional settings. Advances in technology continue to bring forth more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions in the realm of air conditioning products.
Air conditioning machinery is used in the production of various products and in diverse industries where controlling the indoor environment is crucial for processes, product quality, and worker comfort. Some industries and products that rely on air conditioning machinery include:
1. Electronics Manufacturing: Air conditioning is essential in facilities producing electronic components and devices. It helps control the temperature and humidity, ensuring the proper functioning of sensitive electronic equipment.
2. Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities require precise temperature and humidity control to maintain the integrity and stability of medications during production.
3. Food and Beverage: Processing and manufacturing plants in the food and beverage industry use air conditioning to regulate temperature and create hygienic environments for the production and storage of perishable goods.
4. Textile Industry: Textile mills and factories often use air conditioning to control humidity and maintain consistent conditions for the production of textiles and garments.
5. Automotive Manufacturing: Air conditioning is important in automotive production for maintaining comfortable working conditions and ensuring the quality of materials and components.
6. Plastics and Rubber Manufacturing: Industries involved in plastics and rubber production use air conditioning to control temperature and humidity, ensuring the proper curing and molding of materials.
7. Chemical Processing: Facilities involved in chemical production require controlled environments to ensure the safety and quality of chemical processes.
8. Medical Equipment Manufacturing: Air conditioning is crucial in the production of medical devices and equipment to maintain clean and controlled environments.
9. Aerospace Industry: Air conditioning plays a role in the manufacturing of aircraft components and in facilities where aerospace technology is developed.
10. Research Laboratories: Laboratories conducting sensitive research, whether in scientific, medical, or other fields, rely on air conditioning to create stable and controlled conditions for experiments and equipment.

11. Data Centers: Data centers utilize air conditioning to manage the heat generated by servers and electronic equipment, preventing overheating and ensuring reliable operation.
12. Clean Room Environments: Industries like semiconductor manufacturing and nanotechnology require clean room environments with precise temperature, humidity, and particle control, which are achieved through sophisticated air conditioning systems.
In these industries and many others, air conditioning machinery plays a crucial role in creating optimal working conditions, preserving product quality, and ensuring the efficiency and reliability of manufacturing processes.

Air conditioning machinery is used in the production of various products and in diverse industries where controlling the indoor environment is crucial for processes, product quality, and worker comfort. Some industries and products that rely on air conditioning machinery include:

FAQs
How can we reduce the use of air condition machine?
Improving insulation, using energy-efficient appliances, and implementing passive cooling measures can help reduce reliance on air conditioning.
What are the equipment working air condition machinery?
Compressor, condenser, evaporator coil, refrigerant lines, thermostat, air handler, ductwork, fans, filters, ventilation systems, control panels, smart controls, humidifiers/dehumidifiers, variable speed compressors, heat pumps, and eco-friendly refrigerants.
What is air condition machinery equipment?
Air conditioning machinery equipment includes components like compressors, condensers, evaporator coils, thermostats, fans, ductwork, filters, and more, working together to regulate indoor temperature and air quality.
Is the air conditioner a machine?
Yes, an air conditioner is a machine designed to cool and dehumidify indoor air, typically consisting of various components such as a compressor, condenser, evaporator coil, and fans.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14