Wires, Cables & Cable Assemblies
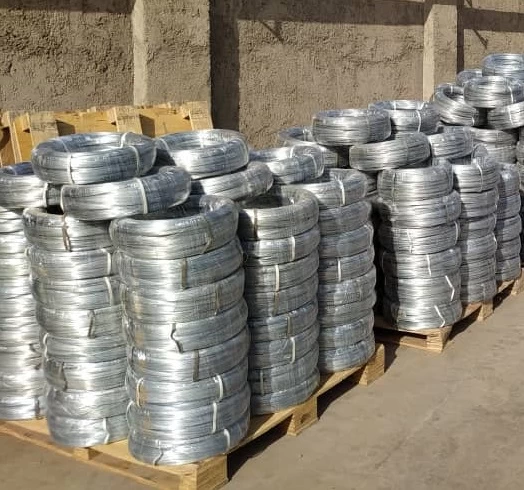
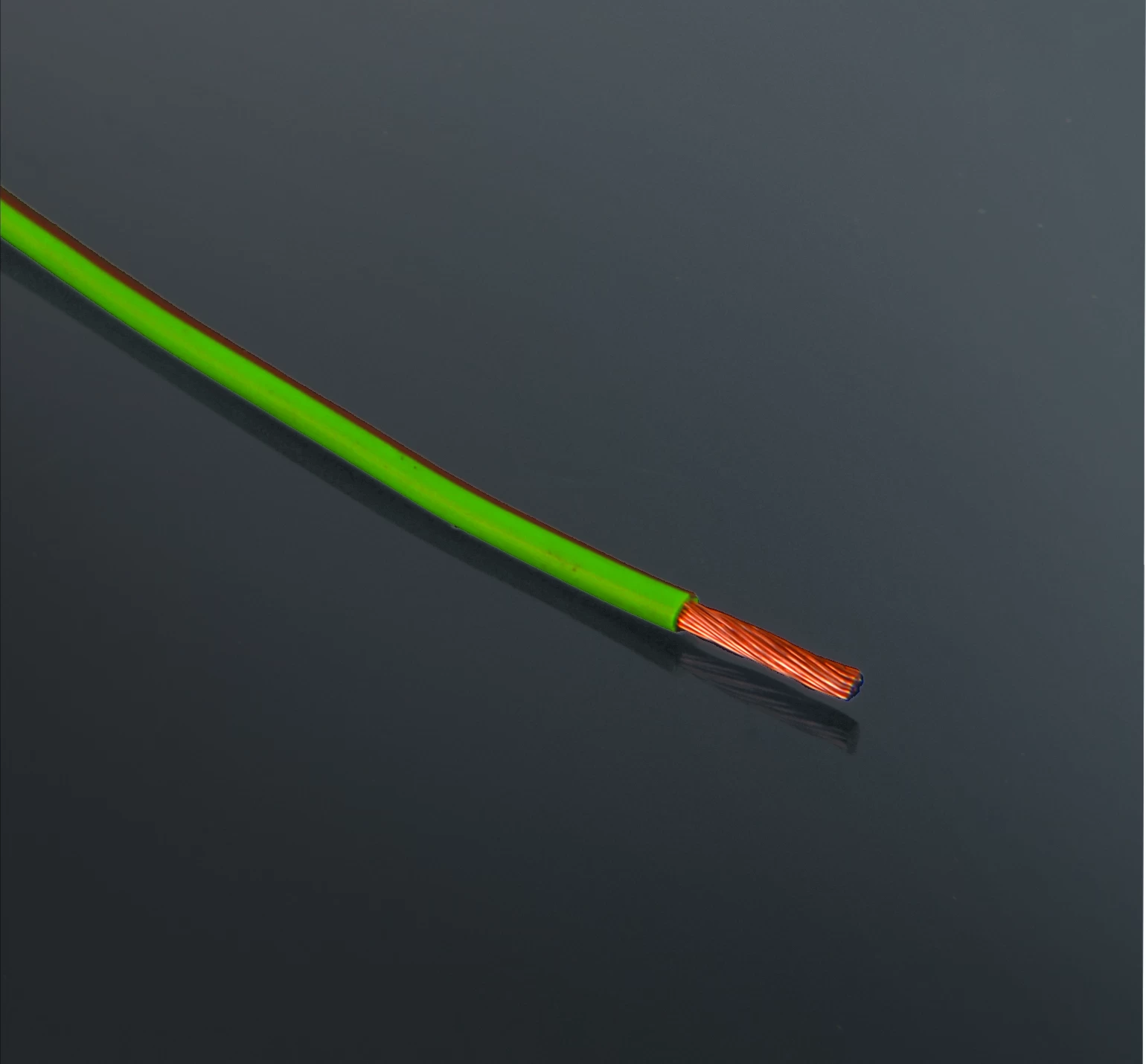
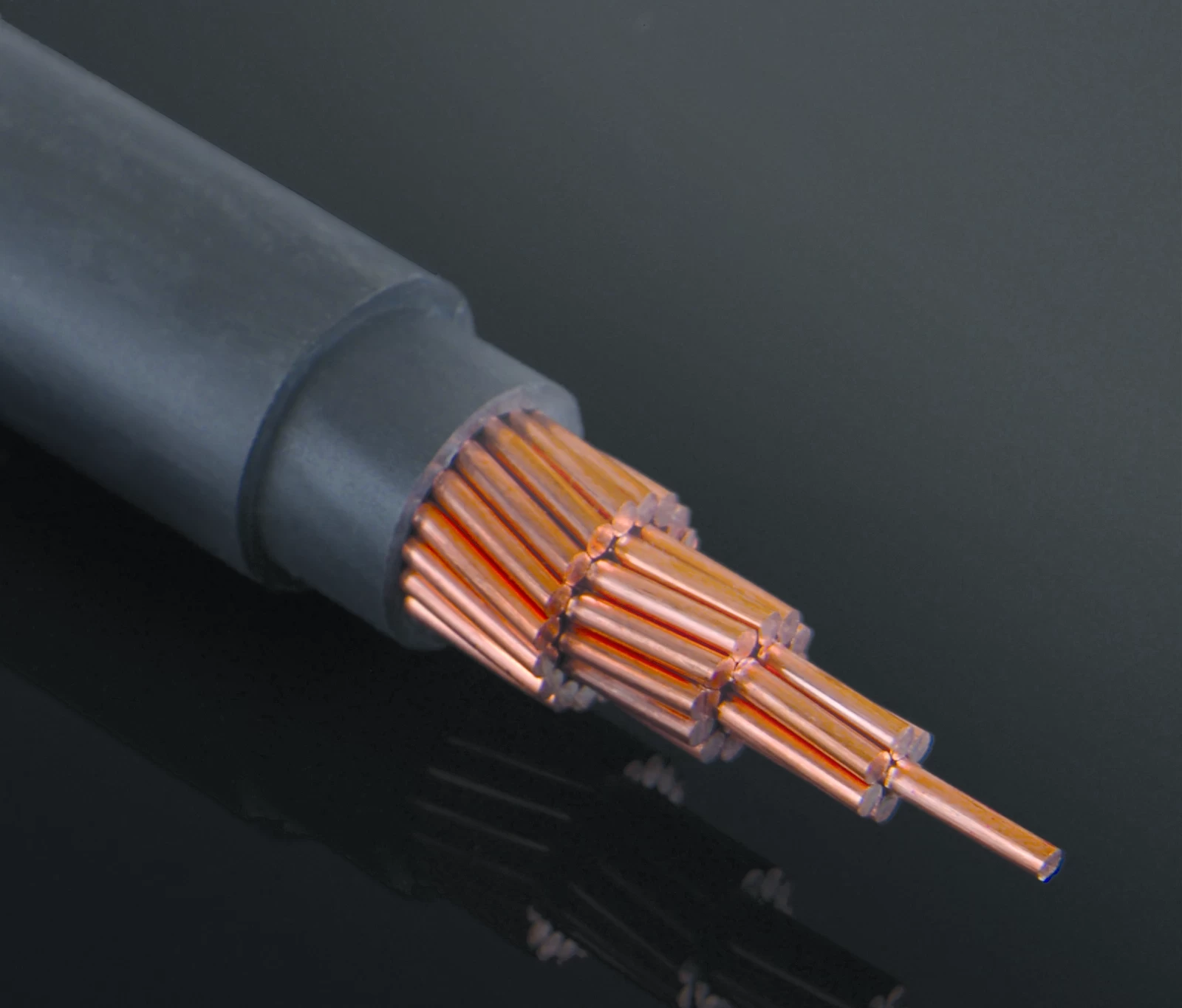
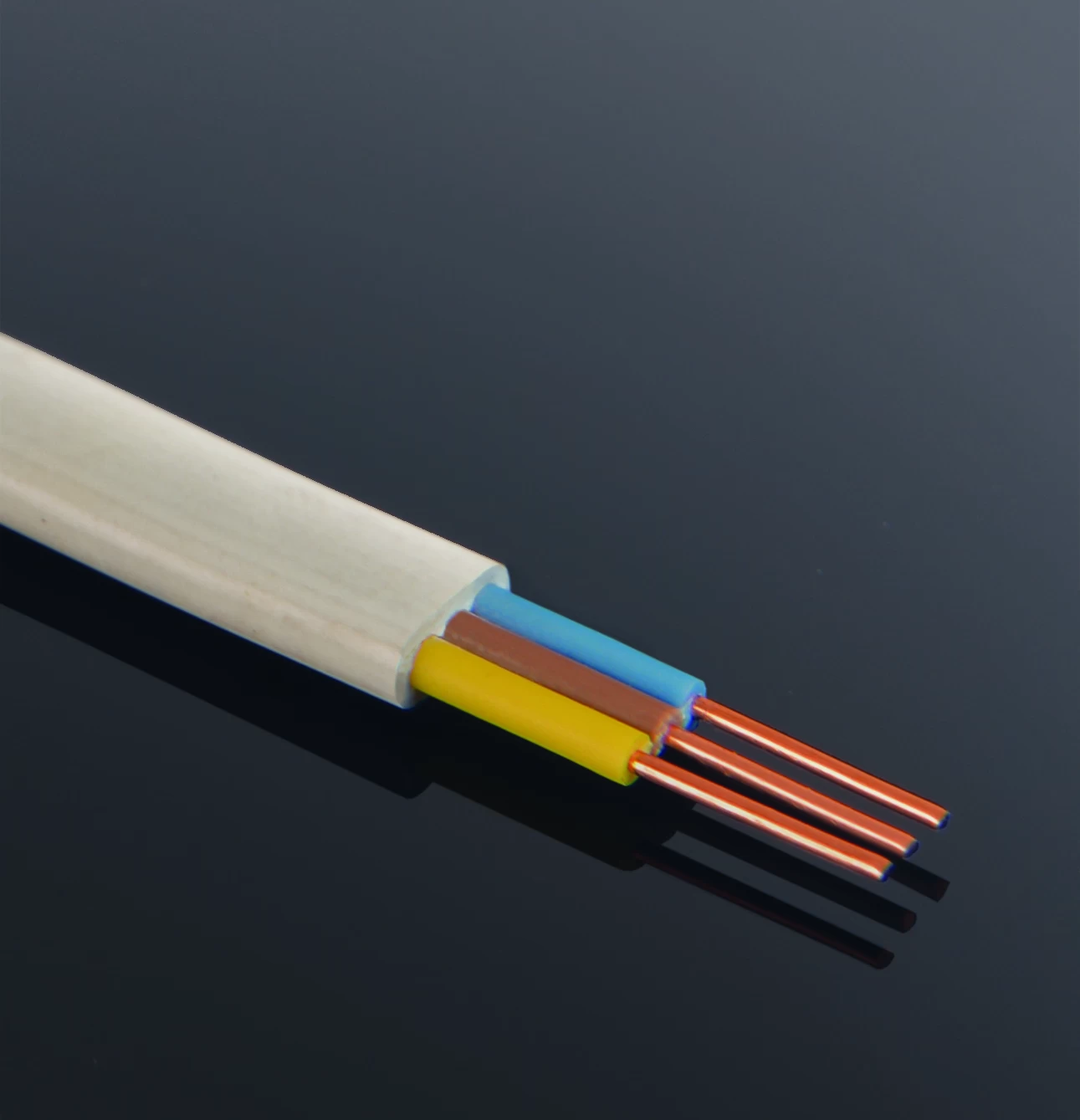
Electronic wire, also known as hookup wire or electrical wire, refers to insulated conductors used to connect electrical components within electronic circuits. These wires are typically made of copper or aluminum conductors surrounded by insulating material, which can be plastic, rubber, or other synthetic materials. Here are some key features of electronic wire:
1. Conductor Material: Copper is the most commonly used conductor material due to its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Aluminum wires are also used in some applications, particularly where weight or cost considerations are important.
2. Insulation: Electronic wires are insulated to prevent electrical short circuits and ensure safe operation within electronic circuits. The insulation material can vary depending on the application requirements, including PVC (polyvinyl chloride), Teflon (PTFE), silicone, and polyethylene.
3. Gauge: The gauge, or thickness, of the wire is specified by its American Wire Gauge (AWG) rating. Thicker wires have lower AWG numbers and can carry higher currents, while thinner wires have higher AWG numbers and are suitable for low-current applications.
4. Stranded vs. Solid: Electronic wire is available in both stranded and solid forms. Stranded wire consists of multiple smaller strands of wire twisted or braided together, offering flexibility and resistance to metal fatigue. Solid wire consists of a single solid conductor and is more rigid but may be more prone to breakage in applications requiring frequent flexing.
5. Color Coding: Electronic wires are often color-coded to facilitate identification and connection within circuits. Common color codes include red for positive voltage, black for ground, and various colors for signal wires or specific functions.
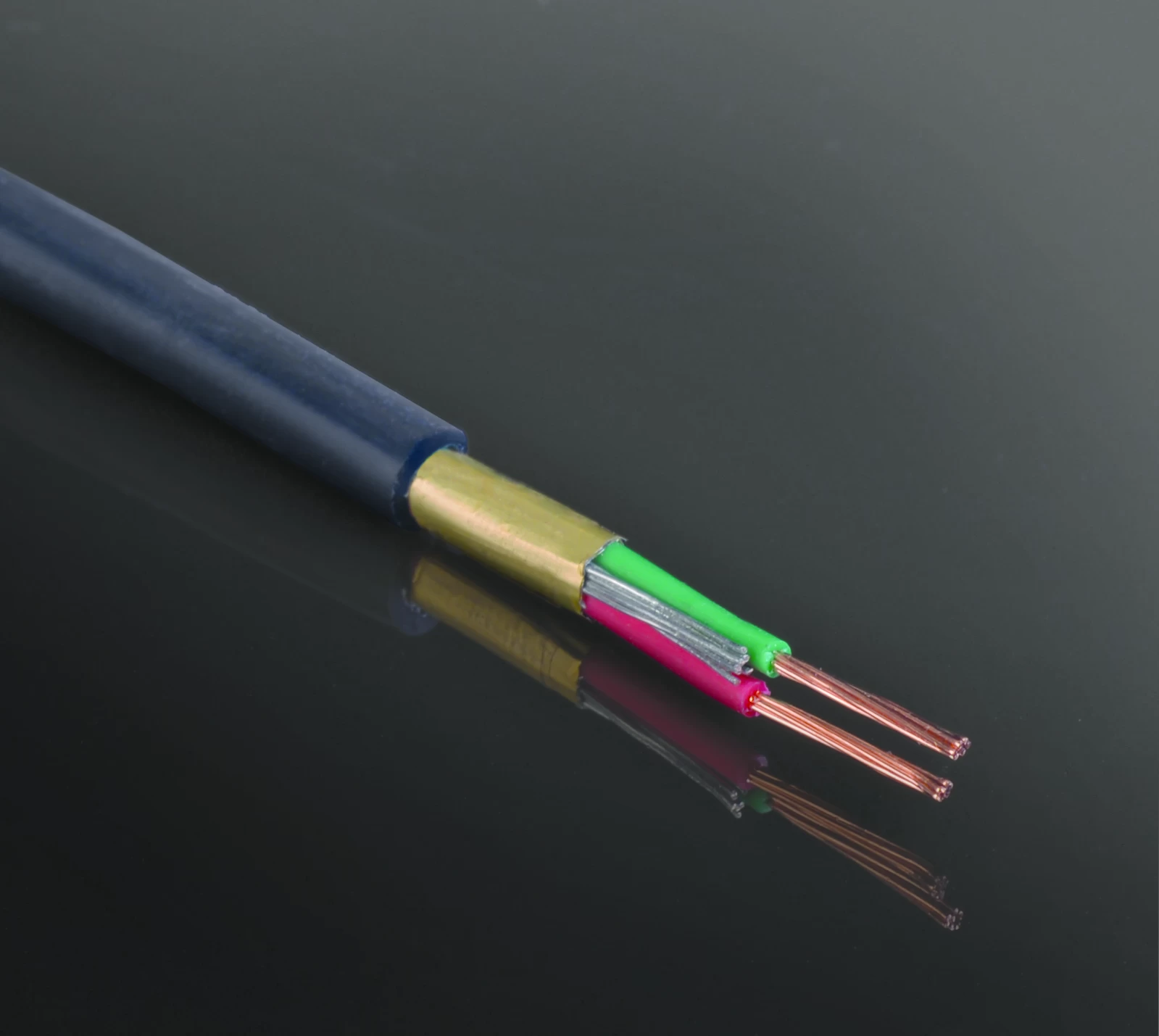
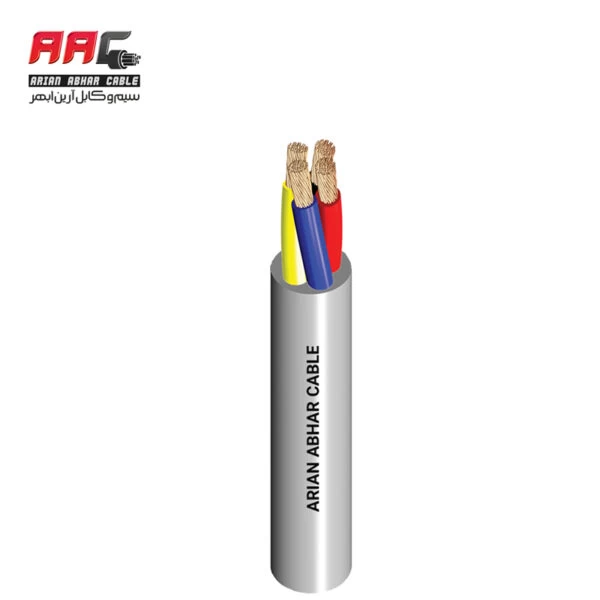
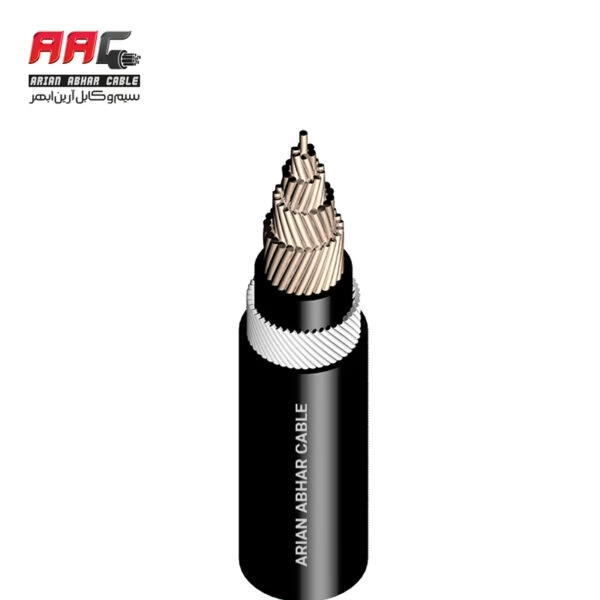
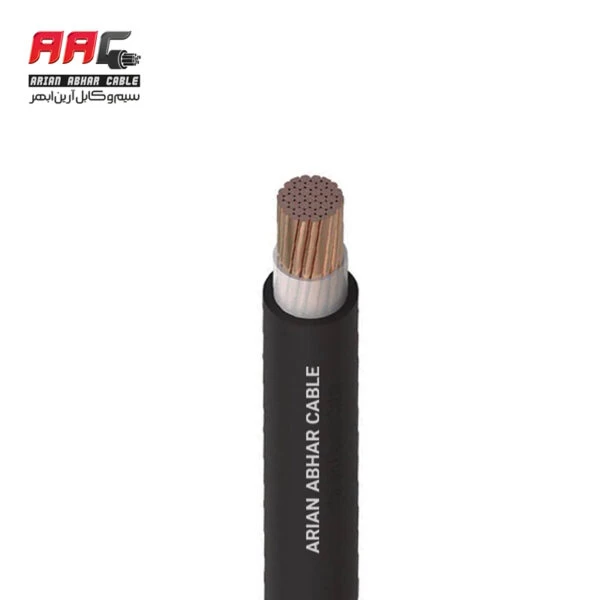
Electronic cables are essential components used to transmit electrical signals or power between devices, components, or systems within electronic equipment and installations. These cables consist of one or more conductors (wires) enclosed in an insulating sheath or jacket and they come in various types and configurations to suit different applications.
Here are some common types of electronic cables:
1. Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating jacket. They are commonly used for transmitting high-frequency signals, such as audio, video, and data, in applications like cable television, internet connections, and telecommunications.
2. Twisted Pair Cable: Twisted pair cables consist of two insulated copper conductors twisted together in a pair configuration. They are widely used in networking and telecommunications for transmitting data signals, such as Ethernet cables (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6) used in local area networks (LANs) and internet connections.
3. Ribbon Cable: Ribbon cables consist of multiple parallel conductors (wires) arranged in a flat ribbon-like configuration, typically with insulation between adjacent conductors. They are commonly used for internal connections in electronic equipment and devices, such as computers, printers, and peripherals.
4. Multiconductor Cable: Multiconductor cables contain multiple insulated conductors bundled together within a single cable jacket. They are used for various applications requiring multiple signal or power connections, such as audio cables, control cables, and power cables in industrial machinery, instrumentation, and consumer electronics.
5. Fiber Optic Cable: Fiber optic cables consist of one or more optical fibers made of glass or plastic enclosed in a protective jacket. They transmit data signals using light pulses and are widely used for long-distance telecommunications, high-speed internet connections, and data networking in environments where electrical interference is a concern.
6. Power Cable: Power cables are designed for transmitting electrical power from a power source to electrical devices or equipment. They typically consist of multiple insulated conductors (wires) encased in a protective jacket or sheath, with larger conductors capable of carrying higher current loads.
7. Flat Cable: Flat cables consist of multiple insulated conductors arranged side by side in a flat configuration, typically with a flexible, ribbon-like structure. They are used in applications where space-saving and flexibility are important, such as internal connections in laptops, mobile devices, and consumer electronics.
_1710869722.jpg)
Electronic cables are crucial components in the design and construction of electronic systems, providing reliable connections for transmitting electrical signals, power, and data between components and devices. The selection of the appropriate cable type depends on factors such as the application requirements, environmental conditions, signal integrity considerations, and compatibility with other components in the system.
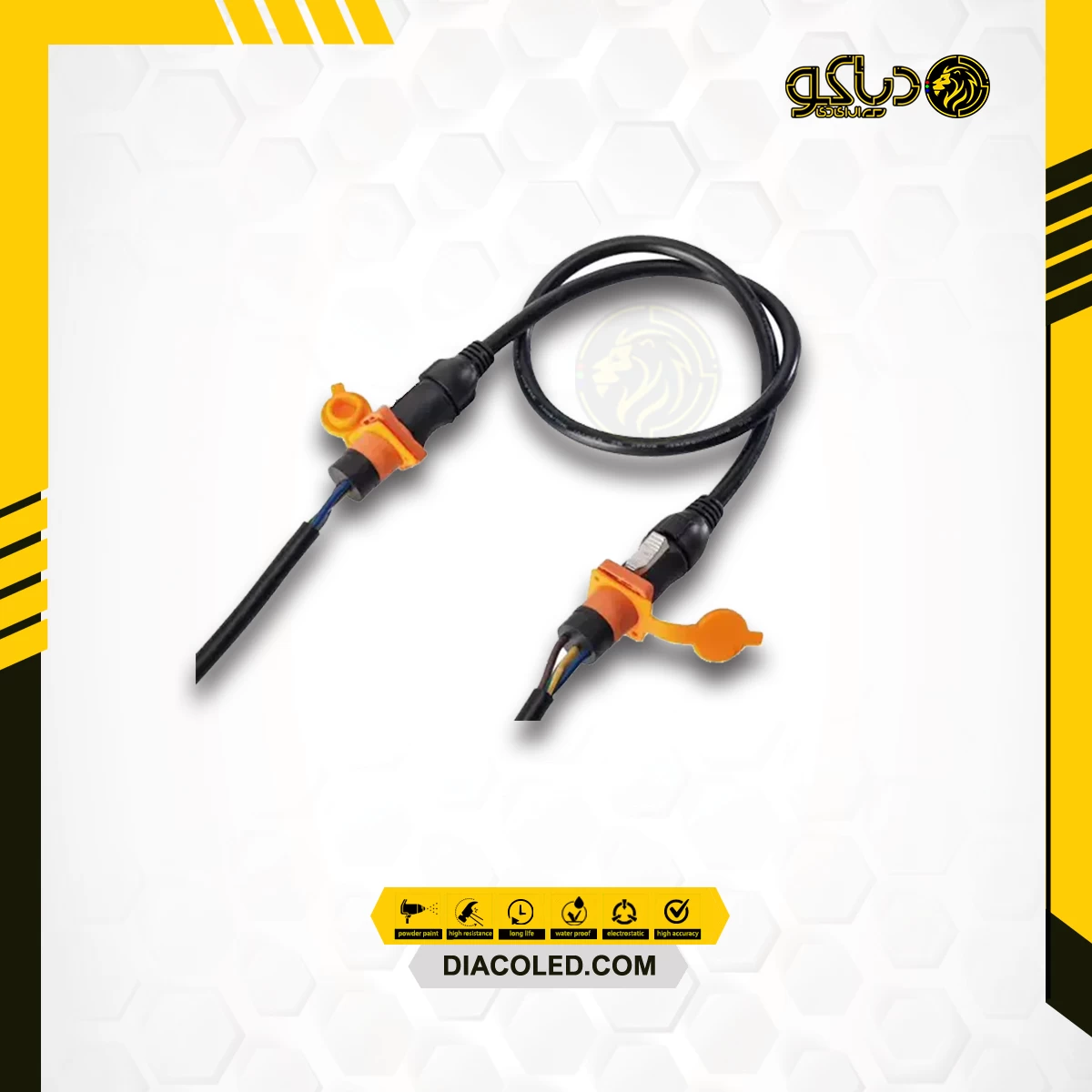
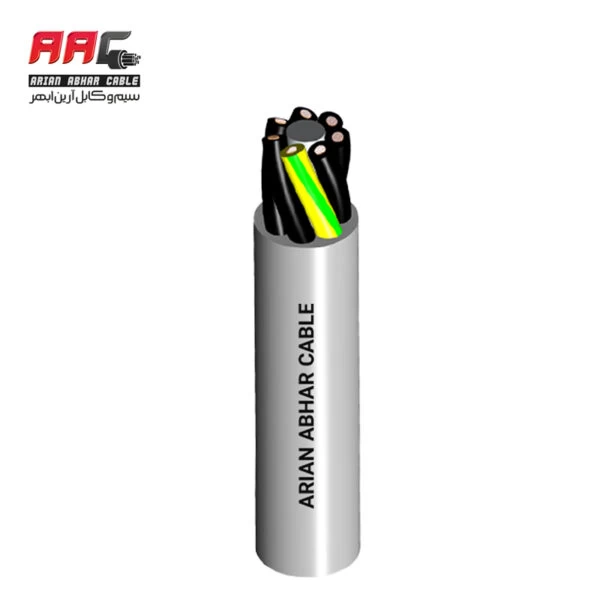
Electronic cable assemblies, also known as wiring harnesses or cable harnesses, are pre-manufactured collections of cables, wires, connectors, and other components organized and bound together into a single unit. These assemblies are used to establish electrical connections between various components within electronic devices, equipment, or systems.
Here are key aspects of electronic cable assemblies:
1. Components: Cable assemblies consist of multiple components, including:
- Cables and Wires: Insulated conductors that carry electrical signals or power.
- Connectors: Interface points that allow the cable assembly to connect to other components or devices.
- Terminals: Points of electrical connection between wires and connectors.
- Splices: Connections between wires within the cable assembly.
- Protection: Additional components such as tubing, sleeves, or wraps may be used for insulation, strain relief, and environmental protection.
2. Customization: Cable assemblies can be customized to meet specific requirements for length, wire gauge, connector type, pinout, and overall configuration. Customization ensures compatibility with the intended application and simplifies installation.
3. Manufacturing Process: Cable assemblies are typically manufactured using automated or semi-automated processes. This includes cutting, stripping, and terminating wires, crimping connectors, and bundling and securing components together.
4. Testing: Quality control measures include testing the continuity, insulation resistance, and electrical performance of the cable assembly to ensure reliability and compliance with specifications.
Twisted cable, also known as twisted pair cable, is a type of electrical cable consisting of two insulated copper wires twisted together in a helical configuration along their length.
Here are some key characteristics and applications of twisted pair cable:
1. Twisting Configuration: Twisted pair cables consist of two insulated conductors twisted together in a regular pattern, typically with a fixed twist rate. The twisting helps reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between adjacent pairs, improving signal integrity.
2. Insulation: Each individual conductor in a twisted pair cable is insulated to prevent short circuits and ensure electrical isolation between the conductors. The insulation material may vary depending on the application requirements and environmental conditions.
3. Categories: Twisted pair cables are classified into different categories based on their performance characteristics and specifications. Common categories include Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, with higher categories offering better performance in terms of bandwidth, crosstalk, and signal transmission capabilities.
4. Applications: Twisted pair cables are widely used for various applications, including:
- Ethernet Networking: Twisted pair cables, such as Cat5e and Cat6 cables, are commonly used for Ethernet networking in homes, offices, and data centers. They provide reliable data transmission for internet connectivity, file sharing, and networked devices.
_1710869758.jpg)
- Telephone Wiring: Twisted pair cables have been traditionally used for telephone wiring to connect telephones, landline phones, and other telecommunications equipment.
- Control Systems: Twisted pair cables are used in control systems, automation, and industrial applications for transmitting control signals and sensor data between devices and controllers.
Electronic cables are essential components used to transmit electrical signals or power between devices, components, or systems within electronic equipment and installations. These cables consist of one or more conductors (wires) enclosed in an insulating sheath or jacket and they come in various types and configurations to suit different applications.
_1710869722.jpg)
Electronic cable assemblies, also known as wiring harnesses or cable harnesses, are pre-manufactured collections of cables, wires, connectors, and other components organized and bound together into a single unit. These assemblies are used to establish electrical connections between various components within electronic devices, equipment, or systems.
- Cables and Wires: Insulated conductors that carry electrical signals or power.
- Connectors: Interface points that allow the cable assembly to connect to other components or devices.
- Terminals: Points of electrical connection between wires and connectors.
- Splices: Connections between wires within the cable assembly.
- Protection: Additional components such as tubing, sleeves, or wraps may be used for insulation, strain relief, and environmental protection.
Twisted cable, also known as twisted pair cable, is a type of electrical cable consisting of two insulated copper wires twisted together in a helical configuration along their length.
- Ethernet Networking: Twisted pair cables, such as Cat5e and Cat6 cables, are commonly used for Ethernet networking in homes, offices, and data centers. They provide reliable data transmission for internet connectivity, file sharing, and networked devices.
_1710869758.jpg)
- Telephone Wiring: Twisted pair cables have been traditionally used for telephone wiring to connect telephones, landline phones, and other telecommunications equipment.
- Control Systems: Twisted pair cables are used in control systems, automation, and industrial applications for transmitting control signals and sensor data between devices and controllers.
FAQs
What are electrical wires made of?
These wires are typically made of copper or aluminum conductors surrounded by insulating material,
Why are electric wires insulated?
Electronic wires are insulated to prevent electrical short circuits and ensure safe operation within electronic circuits.
What are the different types of electrical wires?
Electronic wire is available in both stranded and solid forms
What is the use of electrical cables?
transmit electrical signals or power between devices, components, or systems within electronic equipment and installations.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14






















.webp)