Blanket
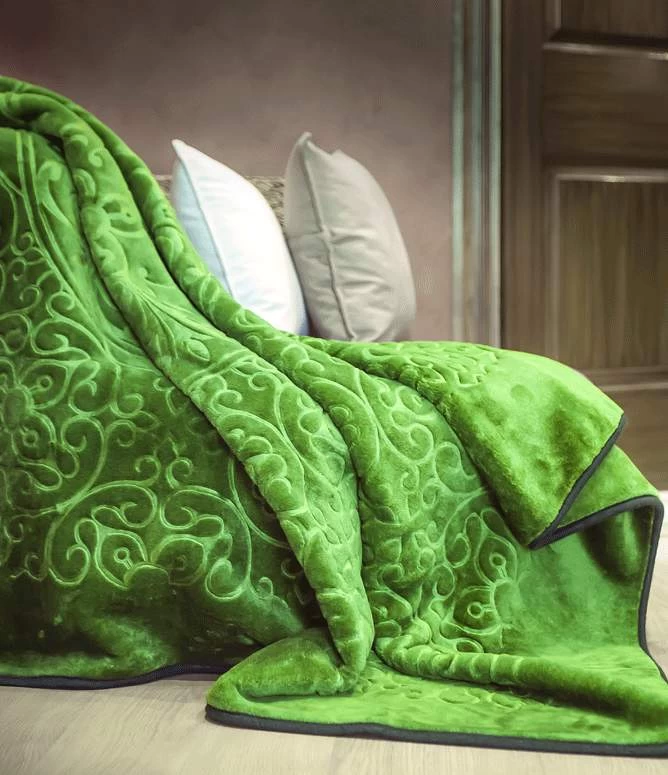
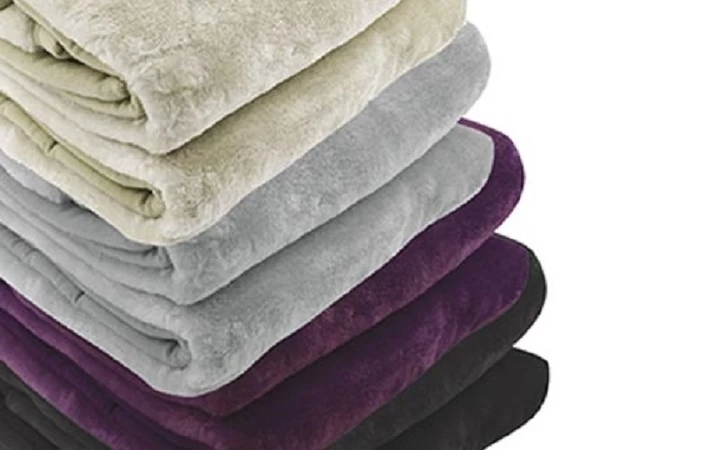
A blanket is a versatile and comforting textile that transcends cultural boundaries, providing warmth and security. Typically made from various materials such as cotton, wool, or fleece, blankets come in an array of colors, patterns, and textures. Beyond their practical use for keeping individuals warm, blankets often hold sentimental value, becoming cherished possessions passed down through generations.
From cozying up on a chilly winter night to creating a makeshift fort for children's imaginative play, blankets serve as more than just a means of insulation. They become integral parts of our daily lives, symbolizing comfort and solace. The act of wrapping oneself in a blanket can evoke a sense of tranquility, offering a retreat from the stresses of the outside world.
Blankets also play a role in cultural practices, such as traditional woven blankets reflecting the rich heritage of various communities. In emergency situations, blankets are distributed as humanitarian aid, emphasizing their fundamental role in ensuring well-being.
In essence, a blanket is not merely a piece of fabric; it embodies warmth, memories, and a universal embrace that transcends its physical form, making it a cherished item in homes worldwide.
Blankets can be made from a variety of materials, each with its own characteristics and purposes. Common materials include:
1. Cotton: Lightweight, breathable, and suitable for all seasons. Cotton blankets are soft and easy to care for.
2. Wool: Known for excellent insulation, wool blankets are warm and can regulate temperature effectively. They are often used in colder climates.
3. Fleece: A synthetic material that is soft, lightweight, and provides warmth. Fleece blankets are often used for casual and outdoor settings.
4. Acrylic: Resembling wool, acrylic blankets are lightweight, hypoallergenic, and can be an affordable alternative.
5. Polyester: Durable and resistant to wrinkles, polyester blankets are easy to maintain. They are often blended with other materials for added comfort.
6. Down or Down Alternative: These blankets are filled with down feathers or synthetic alternatives, providing excellent insulation.
7. Bamboo: An eco-friendly option, bamboo blankets are soft, breathable, and moisture-wicking.

The choice of material depends on personal preferences, climate, and the intended use of the blanket. Each material brings its own set of characteristics, making blankets versatile for various needs and situations.
Blankets are typically made from fabric rather than leather. Leather is not a common material for blankets because it lacks the softness and flexibility associated with traditional blanket materials. Fabrics like cotton, wool, fleece, acrylic, and polyester are more commonly used due to their comfort, warmth, and versatility. Leather is more commonly used in the production of items like furniture, clothing, and accessories, where its durability and unique texture can be better utilized. Blankets made from fabric provide a softer and more comfortable feel, making them suitable for cozying up in various settings.
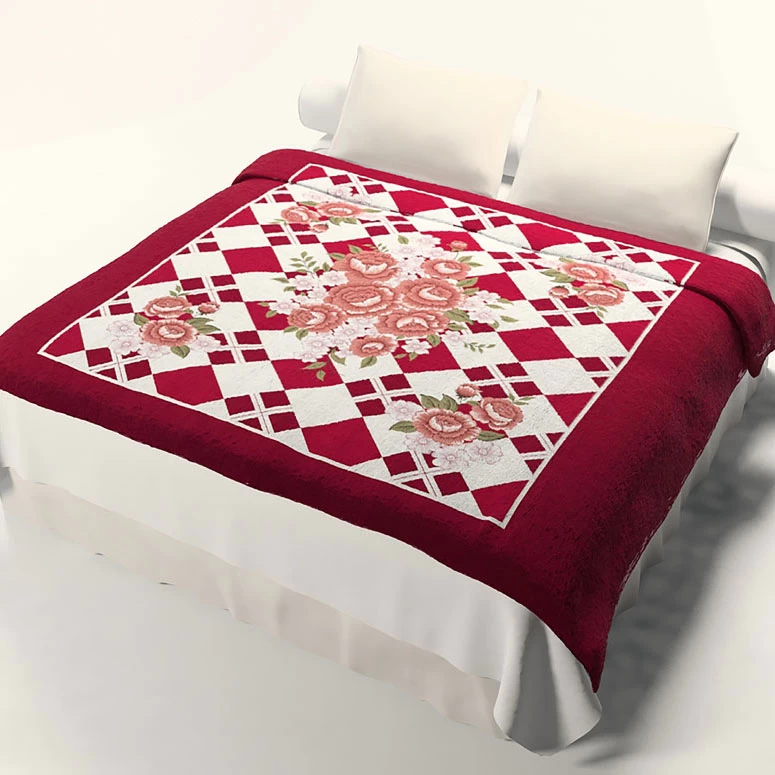
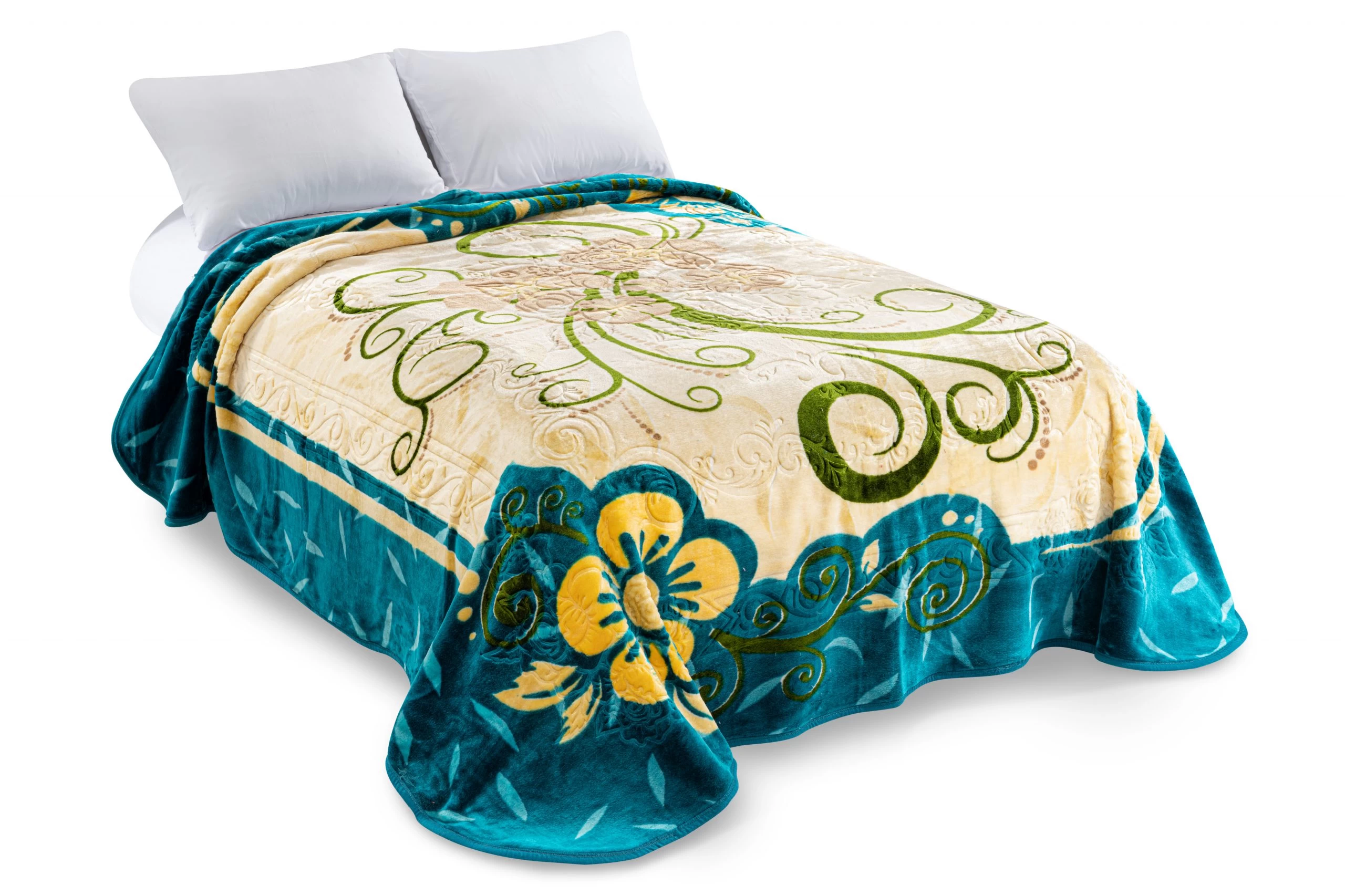
Blankets suitable for beds depend on personal preferences, climate, and the desired level of warmth. Common types of blankets used on beds include:
1. Comforters:Thick, quilted blankets filled with insulating material. They are often used as the top layer on a bed for added warmth.
2. Duvets:Soft, flat blankets that are often used with a duvet cover. Duvets can be filled with down, feathers, or synthetic materials, providing insulation.
3. Quilts: Fabric blankets with a layer of padding or fill in between. Quilts are known for their decorative patterns and can be used alone or layered with other bedding.
4. Throw Blankets: Smaller blankets that add a decorative touch to the bed. They can be folded at the foot of the bed or used for extra warmth when needed.
5. Blanket Sets:Coordinated sets that may include a flat sheet, fitted sheet, blanket, and pillowcases. These sets ensure a cohesive look for the bed.
6. Electric Blankets: Blankets with integrated heating elements. They are ideal for cold climates and can be adjusted to different temperature settings.
When choosing a blanket for a bed, consider the size, material, and the overall aesthetic you want to achieve. It's common to layer different types of blankets to create both visual appeal and customizable warmth.
Blankets, like many other goods, can be exported through various logistics methods, and transshipment is one of them. Transshipment involves the transfer of goods from one vessel or mode of transportation to another during their journey to the final destination. This can occur at intermediate ports or hubs.
In the context of blanket exports, transshipment might happen when blankets manufactured in one country are transported to a port for loading onto a ship, then transferred to another ship at an intermediate port before reaching the final destination. This process is influenced by factors such as shipping routes, available transportation infrastructure, and cost considerations.
Transshipment is a common practice in global trade, allowing for more efficient cargo movement and the optimization of shipping routes. It helps streamline the transportation of goods, including blankets, to different parts of the world.
Blankets have been integral to human civilization for centuries, serving a multitude of purposes beyond their primary function of providing warmth. The historical and cultural significance of blankets extends across various societies, showcasing their versatility and symbolic importance.
1. Practical Warmth:
Blankets were initially developed to offer protection against the cold. Whether fashioned from animal hides, woven textiles, or modern materials, blankets create a barrier against low temperatures. This practical function remains fundamental, especially in regions with cold climates, during outdoor activities, or as part of everyday comfort at home.
2. Shelter and Bedding:
In ancient times, blankets played a crucial role in providing bedding for individuals. Nomadic cultures used animal hides or woven fabrics as makeshift sleeping arrangements. Over time, the development of more sophisticated bed linens evolved, and blankets became essential components of bedding sets, offering not only warmth but also comfort during sleep.
3. Cultural and Traditional Significance:
Blankets hold profound cultural and traditional significance in various societies. Many cultures have distinct blanket-making traditions, with patterns, colors, and weaving techniques passed down through generations. These blankets often serve ceremonial purposes, symbolizing heritage, identity, and the richness of cultural practices.
4. Ceremonial and Ritual Uses:
Blankets have been used in ceremonies and rituals across cultures. In Native American communities, for example, the giving of blankets signified unity, friendship, and peace. In some cultures, blankets are used in religious ceremonies, weddings, or as ceremonial garments, emphasizing their role beyond mere utility.
5. Art and Decoration:
Throughout history, blankets have been appreciated as art forms. Elaborate designs, intricate patterns, and vibrant colors contribute to the aesthetic appeal of blankets. Textile artistry has been a means of creative expression, with artisans using blankets to convey stories, traditions, and artistic visions.

In essence, blankets have transcended their utilitarian origins, becoming woven narratives of human history, culture, and expression. Their multifaceted roles highlight the enduring significance of these seemingly simple yet deeply meaningful textiles in the fabric of human life.

Blankets are typically made from fabric rather than leather. Leather is not a common material for blankets because it lacks the softness and flexibility associated with traditional blanket materials. Fabrics like cotton, wool, fleece, acrylic, and polyester are more commonly used due to their comfort, warmth, and versatility. Leather is more commonly used in the production of items like furniture, clothing, and accessories, where its durability and unique texture can be better utilized. Blankets made from fabric provide a softer and more comfortable feel, making them suitable for cozying up in various settings.
Blankets suitable for beds depend on personal preferences, climate, and the desired level of warmth. Common types of blankets used on beds include:
Blankets, like many other goods, can be exported through various logistics methods, and transshipment is one of them. Transshipment involves the transfer of goods from one vessel or mode of transportation to another during their journey to the final destination. This can occur at intermediate ports or hubs.
Blankets were initially developed to offer protection against the cold. Whether fashioned from animal hides, woven textiles, or modern materials, blankets create a barrier against low temperatures. This practical function remains fundamental, especially in regions with cold climates, during outdoor activities, or as part of everyday comfort at home.
In ancient times, blankets played a crucial role in providing bedding for individuals. Nomadic cultures used animal hides or woven fabrics as makeshift sleeping arrangements. Over time, the development of more sophisticated bed linens evolved, and blankets became essential components of bedding sets, offering not only warmth but also comfort during sleep.
Blankets hold profound cultural and traditional significance in various societies. Many cultures have distinct blanket-making traditions, with patterns, colors, and weaving techniques passed down through generations. These blankets often serve ceremonial purposes, symbolizing heritage, identity, and the richness of cultural practices.
Blankets have been used in ceremonies and rituals across cultures. In Native American communities, for example, the giving of blankets signified unity, friendship, and peace. In some cultures, blankets are used in religious ceremonies, weddings, or as ceremonial garments, emphasizing their role beyond mere utility.
Throughout history, blankets have been appreciated as art forms. Elaborate designs, intricate patterns, and vibrant colors contribute to the aesthetic appeal of blankets. Textile artistry has been a means of creative expression, with artisans using blankets to convey stories, traditions, and artistic visions.

In essence, blankets have transcended their utilitarian origins, becoming woven narratives of human history, culture, and expression. Their multifaceted roles highlight the enduring significance of these seemingly simple yet deeply meaningful textiles in the fabric of human life.
FAQs
What were blankets used for?
Blankets were used for practical warmth, bedding, cultural traditions, ceremonies, artistic expression, comfort, security, humanitarian aid, and even as fashion accessories.
How many types of blankets are there?
There are various types of blankets, including comforters, duvets, quilts, throw blankets, blanket sets, and electric blankets, each serving different purposes and preferences.
Which blanket is most warm?
Wool blankets are often considered the most warm due to their excellent insulation properties. They provide effective warmth and regulate temperature, making them suitable for colder climates.
What is the coolest type of blanket?
Cotton blankets are often considered the coolest type, as they are lightweight, breathable, and suitable for warmer temperatures. They provide comfort without trapping excess heat.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14