Leather
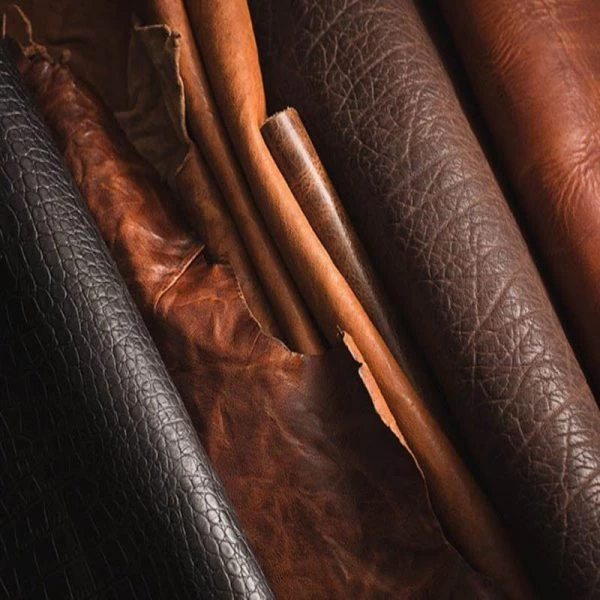
Leather, a timeless material, has been intertwined with human history for millennia. Renowned for its durability and versatility, it has transcended epochs as a symbol of luxury and functionality. From ancient civilizations using animal hides for clothing and shelter to the modern fashion industry crafting exquisite leather goods, its allure endures.
Tanning, the process of transforming raw hides into leather, has evolved over the years. Early methods involved natural substances like plant extracts, but today, advanced chemical processes dominate the industry, balancing efficiency with environmental considerations.
Leather's applications span diverse domains – from the classic leather jacket, boots, and accessories to furniture upholstery and automotive interiors. Each piece narrates a story, as leather ages gracefully, acquiring a unique patina that reflects the wearer's experiences.
Despite its enduring popularity, debates around ethical sourcing and environmental impact persist. Sustainable practices and the rise of alternative materials offer consumers choices aligned with their values. Leather remains an emblem of craftsmanship and style, adapting to the ethos of each era while maintaining its intrinsic charm.

Leather finds application in a myriad of products, showcasing its versatility across various industries. Common uses include:
1. Fashion and Apparel: Leather is prominent in crafting clothing items like jackets, coats, pants, boots, and accessories such as belts, gloves, and handbags.
2. Furniture: Upholstery for sofas, chairs, and other furniture items often utilizes leather due to its durability and aesthetic appeal.
3. Automotive Industry:Car interiors frequently feature leather upholstery, steering wheel covers, and gearshift boots, adding a touch of luxury to vehicles.
4. Footwear:Leather is a traditional material for shoes and boots, valued for its comfort, durability, and ability to mold to the wearer's foot.
5. Accessories:Leather serves as a base material for a range of accessories, including wallets, watch straps, and key holders.
6. Sports Equipment: Certain sports items, like baseball gloves and some types of footballs, incorporate leather for its strength and flexibility.
7. Bookbinding:High-quality books often feature leather covers, combining aesthetics with durability.
8. Interior Design: Leather is utilized in home decor, appearing in items like cushions, rugs, and wall coverings.
Despite its widespread use, there is an increasing trend toward sustainable and alternative materials in response to environmental concerns and ethical considerations.
Leather possesses several unique qualities that contribute to its enduring appeal:
1. Durability:Leather is known for its exceptional strength and resilience, making it long-lasting compared to many other materials.
2. Aesthetic Appeal: The natural texture and grain of leather give it a timeless and sophisticated look. As it ages, leather often develops a distinctive patina, adding character to the item.
3. Comfort:In applications like footwear and furniture, leather tends to conform to the shape of the body or foot, providing a comfortable and personalized fit over time.
4. Breathability:Unlike synthetic materials, leather is breathable, allowing air circulation. This characteristic makes it comfortable to wear in various climates.
5. Versatility: Leather's adaptability is evident in its use across a wide range of products, from fashion to furniture, showcasing its versatility.
6. Luxurious Feel: The tactile experience of genuine leather is often associated with luxury and high-quality craftsmanship, contributing to its desirability.
7. Timeless Style:Leather has transcended fashion trends, maintaining its appeal across generations and adapting to various design aesthetics.
While these qualities make leather highly coveted, discussions around ethical sourcing, environmental impact, and the rise of alternative materials underscore the need for responsible practices in its production and use.
many countries engage in the export of leather and leather products. The leather industry is a global business, with exporting nations supplying raw hides, tanned leather, and finished leather goods to meet international demand. Major exporting countries include India, China, Italy, Brazil, and the United States.
These exports encompass a wide range of products, from raw materials like hides and skins to processed leather used in various industries such as fashion, automotive, and furniture. Additionally, countries with a strong tradition in leather craftsmanship often export high-quality finished goods like shoes, bags, and accessories.
The international leather trade plays a crucial role in connecting producers with markets worldwide, contributing to the global economy. It's worth noting that trends in sustainability and ethical sourcing are influencing trade practices, with some consumers and businesses seeking responsibly produced leather or exploring alternative materials.

High-quality leather is characterized by several key attributes that set it apart from lower-grade counterparts:
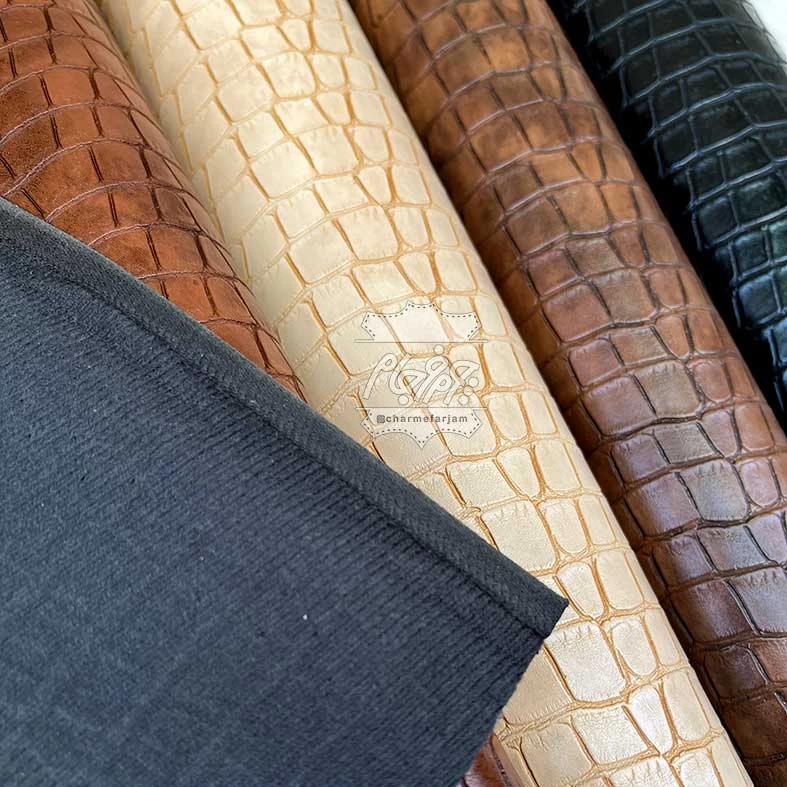
1. Texture and Grain: Premium leather typically features a consistent texture and a well-defined grain pattern. The surface should feel supple and smooth to the touch.
2. Durability: One of the primary advantages of quality leather is its durability. It should withstand wear and tear gracefully, developing a patina over time rather than showing signs of damage.
3. Natural Aroma: Genuine leather has a distinctive, pleasant aroma. This scent is often associated with the natural tanning process and is a sign of authentic, high-quality material.
4. Flexibility and Softness: Quality leather is flexible and soft, molding to the contours of the body or object it covers. This characteristic contributes to comfort and a luxurious feel.
5. Color Depth and Consistency: Premium leather maintains a rich and deep color. The hue should be consistent across the entire surface, indicating quality dyeing processes.
6. Absence of Imperfections: High-quality leather should be free from major imperfections such as scars, blemishes, or noticeable wrinkles. Any natural markings should be minimal and contribute to the character of the leather.
7. Resistance to Fading:Quality leather is less prone to fading when exposed to sunlight or other environmental factors. It retains its color and luster over time.
8. Tanning Process:The tanning process significantly influences leather quality. Vegetable tanning and other natural methods are often associated with higher quality due to their environmental sustainability and the resulting richness of the leather.
9. Craftsmanship: The way leather is cut and assembled into products reflects craftsmanship. High-quality leather goods often exhibit precise stitching, attention to detail, and careful construction.
Understanding these characteristics helps consumers make informed choices when selecting leather products and ensures they receive items that are both aesthetically pleasing and durable.

Leather possesses several unique qualities that contribute to its enduring appeal:
many countries engage in the export of leather and leather products. The leather industry is a global business, with exporting nations supplying raw hides, tanned leather, and finished leather goods to meet international demand. Major exporting countries include India, China, Italy, Brazil, and the United States.

FAQs
What is special about leather?
Durability, aesthetic appeal, comfort, breathability, versatility, luxurious feel, timeless style.
Why is leather popular?
Durable, versatile, stylish, luxurious feel, adaptable to various products, timeless appeal.
Which animal leather is best?
Preference varies, but cowhide is common for its durability, while exotic leathers like alligator or ostrich offer luxury.
What's the strongest leather?
Kangaroo leather is known for its strength-to-weight ratio, making it exceptionally strong despite being lightweight.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14