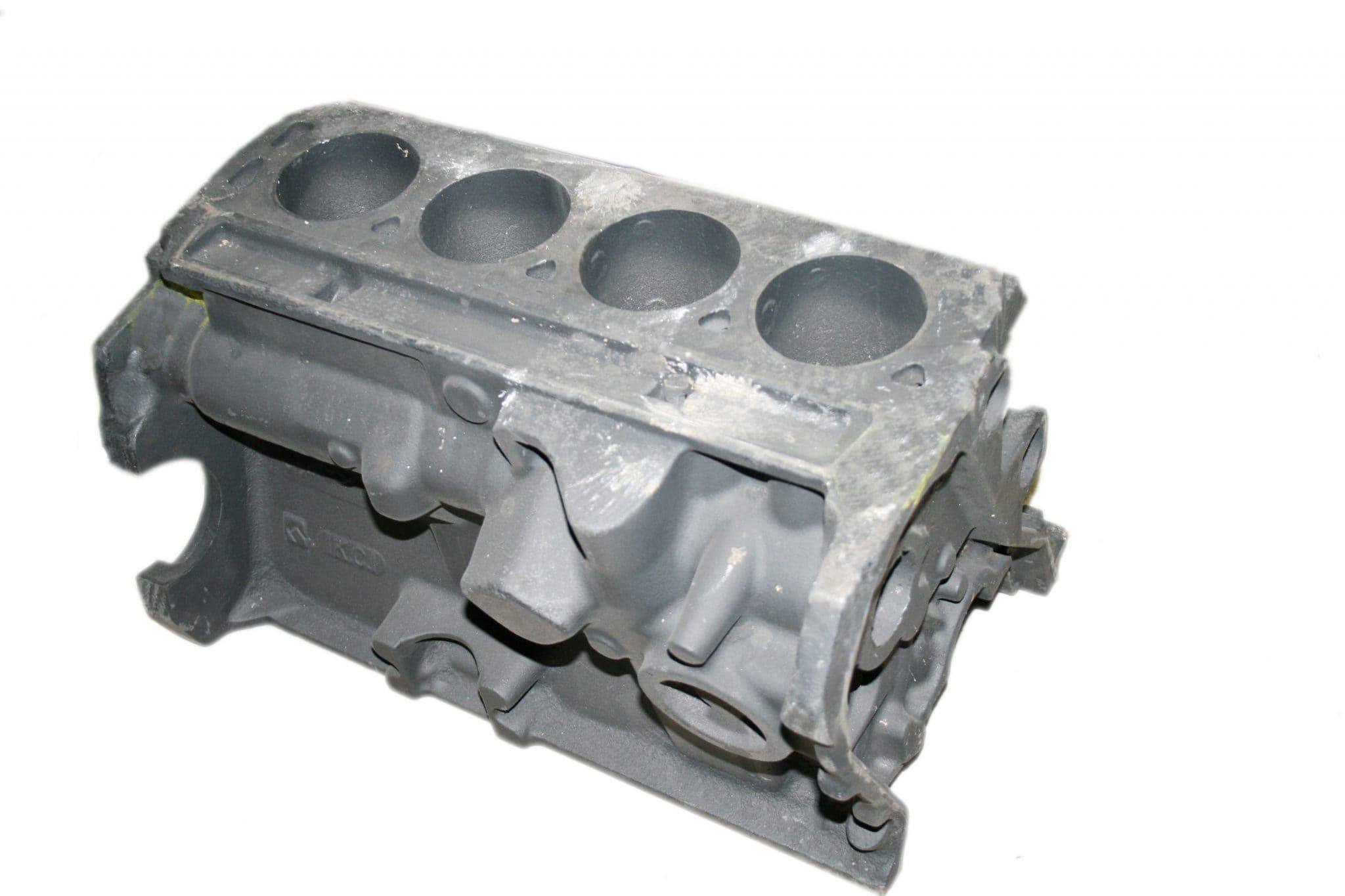
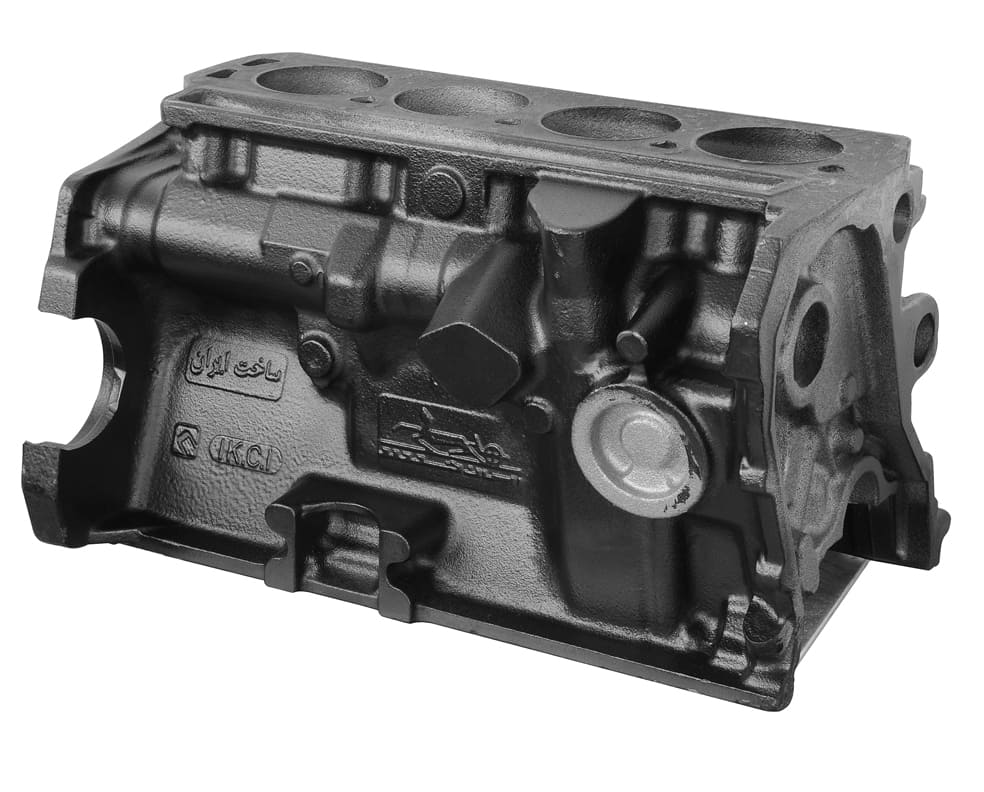
The cylinder block is actually the skeleton and main body of an internal combustion engine that accounts for most of the engine's volume. This part of the engine is also considered a kind of base and support for other components, such as the installation location of components such as the crankshaft, piston rings, connecting rods, cylinder head, cartel, and gas manifold. Therefore, it can be said that the philosophy of producing and using the cylinder block is to create integration between the various components of the engine through it and the plurality of cylinders. In other words, the cylinder is almost the most important part in the event of combustion, but a cylinder alone cannot provide the power needed by the vehicle, and in order for it to move, the cylinders need to be arranged in a regular arrangement. This arrangement is adjusted by the cylinder block. In this way, the cylinder block, which is a piece made of cast iron, is designed in such a way that it has cylindrical holes in it, while having the necessary spaces for installing other components and the necessary channels for the passage of oil and coolant. These hollow cylinders form the walls of the cylinders. The cylinder, which is formed by placing the cylinder head gasket and the cylinder head to complete the walls, forms the combustion chamber in which the piston moves up and down and, while providing the necessary compression of the fuel and oil mixture on the block and to cause combustion, it also transfers the force created by the explosion to other parts. In general, the function of the cylinder block can be summarized into the following 5 things:
It is a place for the piston to move
Chemical energy is converted into thermal energy
Thermal energy is converted into pressure
Conversion of pressure into force
Conversion of force into piston movement
Few companies are able to produce cylinder blocks due to the complexity of production and the need for high dimensional tolerances.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14

 Automotive Cast Parts
Automotive Cast Parts