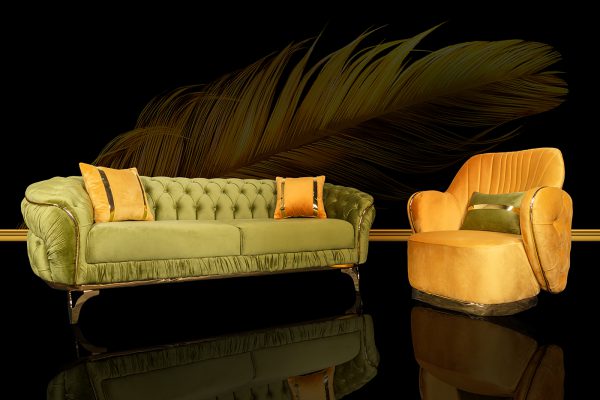
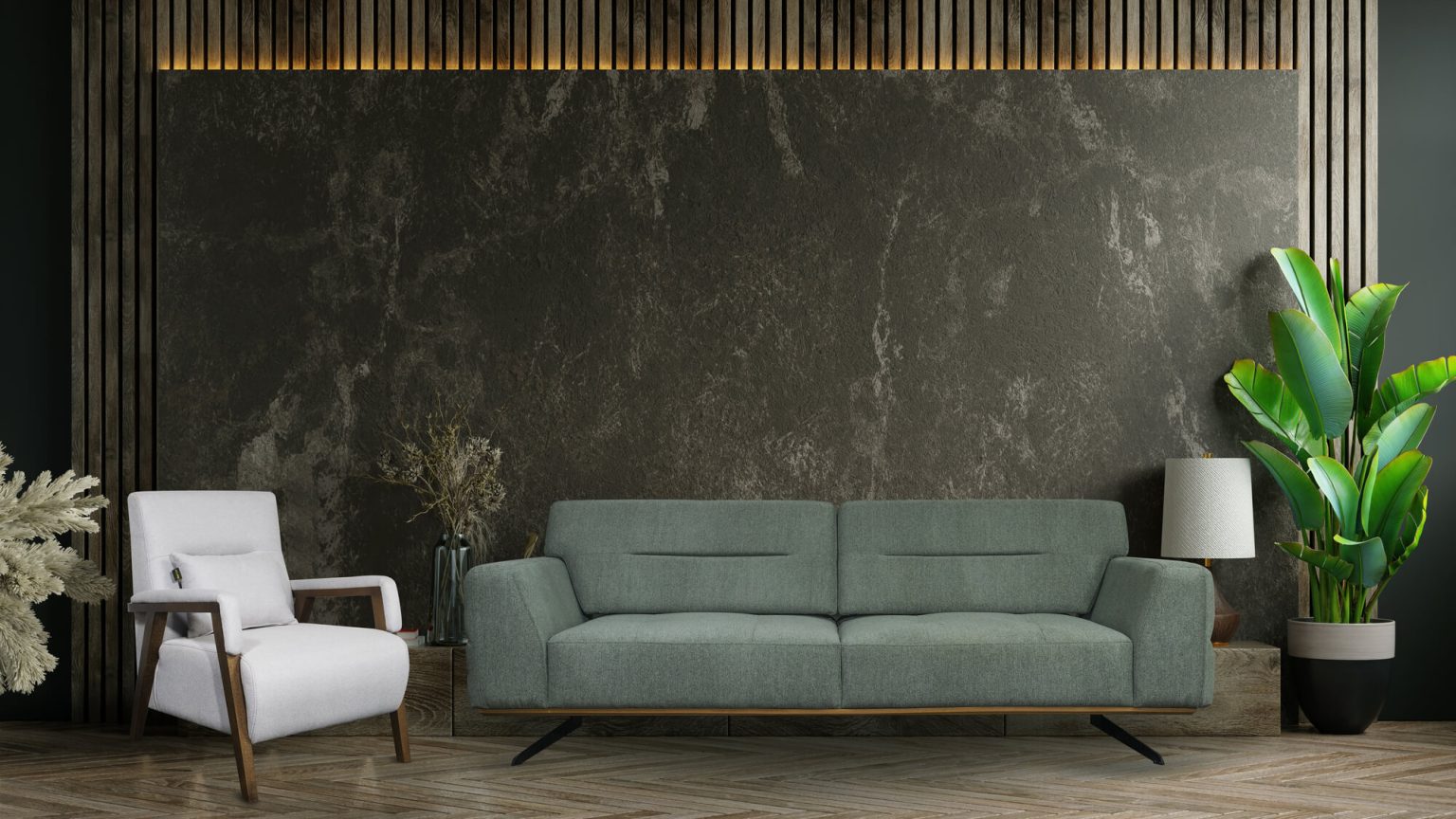
Living Room Sofa
Living room sofas are a key piece of furniture that serve as the central seating area in most homes.
They come in a wide variety of styles, materials, and sizes to suit different decor preferences and room dimensions.
Some common sofa types include:
- Sectional sofas - These modular sofas can be configured in different shapes to fit the layout of a room. They often include chaise lounge sections.
- Loveseat sofas - Smaller two-seat sofas that work well in tighter spaces.
- Sleeper sofas - Sofas that fold out into a bed, providing guest sleeping accommodations.
- Recliner sofas - Sofas with built-in reclining mechanisms in the seats.
Sofas are typically upholstered in fabrics like leather, microfiber, or linen. Popular color choices include neutral tones like gray, beige, and navy. Sofas can also feature decorative elements like tufting, nailhead trim, or turned legs.

When selecting a sofa, key considerations are the size of the room, the desired seating capacity, the overall aesthetic, and the budget. Proper measurements are important to ensure the sofa fits well in the space. High-quality, well-constructed sofas can be a significant investment but can also last for many years.
Here are some of the key differences between indoor and outdoor sofas and furniture:
Materials:
- Outdoor furniture is designed to withstand exposure to the elements, so it uses more durable materials like weather-resistant fabrics, rust-proof metals, and moisture-resistant woods.
- Common outdoor sofa materials include synthetic wicker, aluminum, teak, and fade-resistant fabrics like Sunbrella.
- Indoor sofas typically use more delicate materials like cotton, leather, and wood that can be damaged by moisture, UV rays, and extreme temperatures.
Construction:
- Outdoor furniture is built to be more sturdy and withstand heavy use, with reinforced frames and joints.
- Outdoor sofas often have removable cushions that can be easily cleaned or replaced.
- Indoor sofas focus more on comfort and aesthetics rather than weatherproofing.
Styling:
- Outdoor furniture has a more casual, relaxed aesthetic suited for patio, porch, or garden settings.
- Outdoor sofas tend to have clean, minimalist lines and don't require decorative elements like tufting or skirts.
- Indoor sofas have a wider range of traditional, modern, and eclectic design styles to match interior home decor.
Maintenance:
- Outdoor furniture requires more regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent weathering, mildew, and corrosion.
- Outdoor sofas often need to be covered or stored during harsh weather conditions.
- Indoor sofas only need occasional light cleaning and can be placed anywhere in the home.
Price:
- High-quality outdoor furniture, including sofas, tends to be more expensive than comparable indoor pieces.
- The durability and weatherproofing of outdoor furniture justifies the higher price tag.
So in summary, outdoor sofas and furniture are engineered to withstand environmental stresses, have a more casual aesthetic, and require more maintenance compared to indoor varieties. The differences in materials, construction, and styling all support the unique needs of outdoor living spaces.
Sofas are considered furniture, not home appliances.
The key differences between sofas and home appliances are:
Purpose:
- Sofas are pieces of furniture primarily used for seating and lounging in a living room or other indoor space.
- Home appliances are electronic devices used to perform specific household functions, like cooking, cleaning, cooling, etc.
Mobility:
- Sofas are stationary, large pieces of furniture that are not meant to be frequently moved around.
- Home appliances are usually compact, self-contained devices that can be more easily relocated as needed.
Power Source:
- Sofas do not require any electricity or power source to function.
- Most home appliances rely on electricity, gas, or other power sources to operate.
Installation:
- Sofas are freestanding pieces that can simply be placed in a room.
- Many home appliances require professional installation, plumbing, or electrical work.
Lifespan:
- Sofas are durable furniture pieces meant to last for years or decades with proper care.
- Home appliances typically have a shorter expected lifespan of 5-15 years on average.
So in summary, sofas fall squarely into the furniture category, while home appliances are a distinct class of household devices used for specific functional purposes. Sofas are considered fundamental furnishings rather than powered appliances. This distinction is important when it comes to purchasing, placement, maintenance, and replacement of these different types of home goods.

Sofas have some distinct design and material differences compared to other common types of furniture:
1. Frame Construction:
- Sofas typically have a more robust, reinforced frame made of solid wood, engineered wood, or metal to support the weight of multiple occupants.
- Other furniture like chairs or side tables often have simpler, lighter frame materials.
2. Upholstery:
- Sofas are almost always upholstered with fabrics, leather, or microfiber to provide comfort and a finished look.
- Tables, desks, and bookcases usually have exposed wood, glass, or other non-upholstered surfaces.
3. Size and Scale:
- Sofas are generally larger, deeper, and more substantial in size compared to other living room furniture.
- This allows them to accommodate multiple people sitting comfortably.
4. Cushioning:
- Sofas have thick, multilayer cushions made of high-density foam, springs, and batting to create a plush, supportive seat.
- Other furniture may have thin, less complex cushioning or none at all.
5. Styling:
- Sofas often feature decorative elements like tufting, nailhead trim, skirts, and turned legs to enhance their aesthetic.
- Accent chairs, ottomans, and coffee tables typically have simpler, more minimalist designs.
6. Modularity:
- Sectional and modular sofas can be rearranged into different configurations to fit a space.
- Most other furniture pieces are single, fixed units.
7. Longevity:
- High-quality sofas are built to last for decades with proper care and maintenance.
- Other furniture may have a shorter expected lifespan.
So in summary, the robust frame, upholstered construction, larger scale, and flexible modularity of sofas distinguish them from other living room furnishings that serve more specialized functions. This makes sofas a central, versatile piece within the overall furniture arrangement.

- Outdoor furniture is designed to withstand exposure to the elements, so it uses more durable materials like weather-resistant fabrics, rust-proof metals, and moisture-resistant woods.
- Common outdoor sofa materials include synthetic wicker, aluminum, teak, and fade-resistant fabrics like Sunbrella.
- Indoor sofas typically use more delicate materials like cotton, leather, and wood that can be damaged by moisture, UV rays, and extreme temperatures.
- Outdoor furniture is built to be more sturdy and withstand heavy use, with reinforced frames and joints.
- Outdoor sofas often have removable cushions that can be easily cleaned or replaced.
- Indoor sofas focus more on comfort and aesthetics rather than weatherproofing.
- Outdoor furniture has a more casual, relaxed aesthetic suited for patio, porch, or garden settings.
- Outdoor sofas tend to have clean, minimalist lines and don't require decorative elements like tufting or skirts.
- Indoor sofas have a wider range of traditional, modern, and eclectic design styles to match interior home decor.
- Outdoor furniture requires more regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent weathering, mildew, and corrosion.
- Outdoor sofas often need to be covered or stored during harsh weather conditions.
- Indoor sofas only need occasional light cleaning and can be placed anywhere in the home.
- High-quality outdoor furniture, including sofas, tends to be more expensive than comparable indoor pieces.
- The durability and weatherproofing of outdoor furniture justifies the higher price tag.
- Sofas are pieces of furniture primarily used for seating and lounging in a living room or other indoor space.
- Home appliances are electronic devices used to perform specific household functions, like cooking, cleaning, cooling, etc.
- Sofas are stationary, large pieces of furniture that are not meant to be frequently moved around.
- Home appliances are usually compact, self-contained devices that can be more easily relocated as needed.
- Sofas do not require any electricity or power source to function.
- Most home appliances rely on electricity, gas, or other power sources to operate.
- Sofas are freestanding pieces that can simply be placed in a room.
- Many home appliances require professional installation, plumbing, or electrical work.
- Sofas are durable furniture pieces meant to last for years or decades with proper care.
- Home appliances typically have a shorter expected lifespan of 5-15 years on average.

- Sofas typically have a more robust, reinforced frame made of solid wood, engineered wood, or metal to support the weight of multiple occupants.
- Other furniture like chairs or side tables often have simpler, lighter frame materials.
- Sofas are almost always upholstered with fabrics, leather, or microfiber to provide comfort and a finished look.
- Tables, desks, and bookcases usually have exposed wood, glass, or other non-upholstered surfaces.
- Sofas are generally larger, deeper, and more substantial in size compared to other living room furniture.
- This allows them to accommodate multiple people sitting comfortably.
- Sofas have thick, multilayer cushions made of high-density foam, springs, and batting to create a plush, supportive seat.
- Other furniture may have thin, less complex cushioning or none at all.
- Sofas often feature decorative elements like tufting, nailhead trim, skirts, and turned legs to enhance their aesthetic.
- Accent chairs, ottomans, and coffee tables typically have simpler, more minimalist designs.
- Sectional and modular sofas can be rearranged into different configurations to fit a space.
- Most other furniture pieces are single, fixed units.
- High-quality sofas are built to last for decades with proper care and maintenance.
- Other furniture may have a shorter expected lifespan.
FAQs
What are the most common sofa materials?
The most common sofa materials are leather, microfiber, and fabric upholstery, as well as solid wood or engineered wood frames.
How do you choose the right size sofa for a living room?
To choose the right sized sofa, measure the available space in your living room and consider the room's dimensions, the number of seats needed, and the overall furniture layout.
What are the benefits of a modular or sectional sofa?
Modular and sectional sofas offer the flexibility to configure the seating arrangement to fit your space, accommodate different household needs, and adapt as your living room changes over time.
How do you care for and maintain a living room sofa?
Proper sofa maintenance involves regular vacuuming, spot cleaning, fluffing cushions, and protecting from direct sunlight to extend the life of the upholstery and frame.