Plastic Products
Plastic products encompass a wide range of items made from synthetic polymers, also known as plastics. These products are ubiquitous in modern society and serve various purposes across numerous industries. Plastic products are valued for their versatility, durability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness. They are used in everyday items as well as in industrial applications.
Here are some common categories of plastic products:
1. Packaging : Plastic packaging is used extensively in the food and beverage industry, pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, and more. Examples include bottles, containers, bags, films, wraps, and clamshells.
2. Construction Materials : Plastics are used in construction for various purposes, including pipes, fittings, insulation materials, roofing materials, flooring, window frames, and decorative panels.
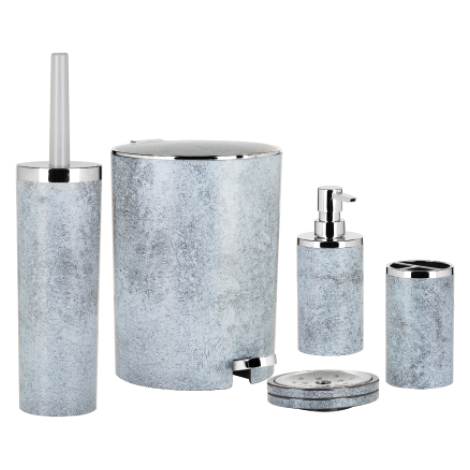
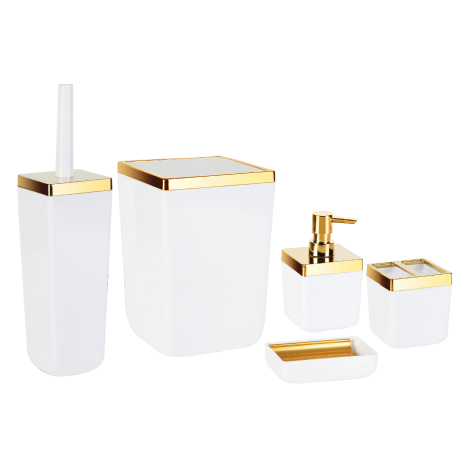
3. Consumer Goods : Plastic products are found in a wide range of consumer goods such as toys, kitchenware, utensils, storage containers, furniture, electronics housings, and appliances.
4. Automotive Parts : Plastics play a significant role in the automotive industry, where they are used for interior and exterior components, dashboards, door panels, bumpers, trim pieces, and more.
5. Medical Devices : Plastics are extensively used in the healthcare industry for manufacturing medical devices and equipment such as syringes, IV bags, medical tubing, surgical instruments, and prosthetic devices.
6. Textiles and Apparelm: Synthetic fibers derived from plastics are used in the textile industry for making clothing, upholstery, carpets, and other textile products.
7. Electronics : Plastics are used in the manufacturing of electronic devices and components such as casings, housings, connectors, insulators, and display screens.
8. Sports and Recreation : Plastic products are used in various sports and recreational equipment such as helmets, protective gear, sports bottles, kayak hulls, and camping gear.
9. Agriculture: Plastics are used in agriculture for greenhouse films, irrigation tubing, mulch films, seedling trays, and agricultural nets.
10. Packaging and Printing: Plastic products include packaging materials such as shrink wrap, bubble wrap, stretch film, and packaging trays. In printing, plastic substrates like vinyl, PVC, and polyester films are used for signage, banners, labels, and graphics.
These are just a few examples of the diverse range of plastic products that are integral to modern life and industry. The versatility and adaptability of plastics continue to drive innovation and development across various sectors.
Plastic packaging refers to the use of plastic materials to package, store, and protect products. Plastic packaging comes in various forms, including bottles, containers, bags, films, wraps, trays, and clamshells. It is widely used across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, personal care, household goods, and industrial products due to its versatility, durability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness.
_1710693899.jpg)
Plastic packaging offers several advantages:
1. Versatility : Plastic packaging can be molded into various shapes and sizes to accommodate different products and applications.
2. Durability : Plastic packaging is durable and resistant to breakage, making it ideal for transporting and storing products safely.
3. Lightweight : Plastic packaging is lightweight, which reduces transportation costs and energy consumption during shipping.
4. Transparency : Many plastic packaging materials are transparent, allowing consumers to see the product inside, which can be appealing for marketing purposes.
5. Barrier Properties : Plastic packaging can provide barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and other environmental factors, helping to extend the shelf life of products.
6. Cost-Effectiveness : Plastic packaging is often more cost-effective than alternative materials such as glass or metal.
Despite its benefits, plastic packaging also poses environmental challenges, particularly related to plastic waste and pollution. Single-use plastic packaging, in particular, has come under scrutiny due to its contribution to plastic pollution in oceans and landfills. As a result, there is increasing interest in sustainable packaging solutions, including biodegradable plastics, recycled plastics, and alternative materials such as paper and compostable materials.
Efforts to reduce plastic packaging waste include initiatives to promote recycling, improve packaging design to minimize waste, and develop innovative materials and technologies for more sustainable packaging solutions.
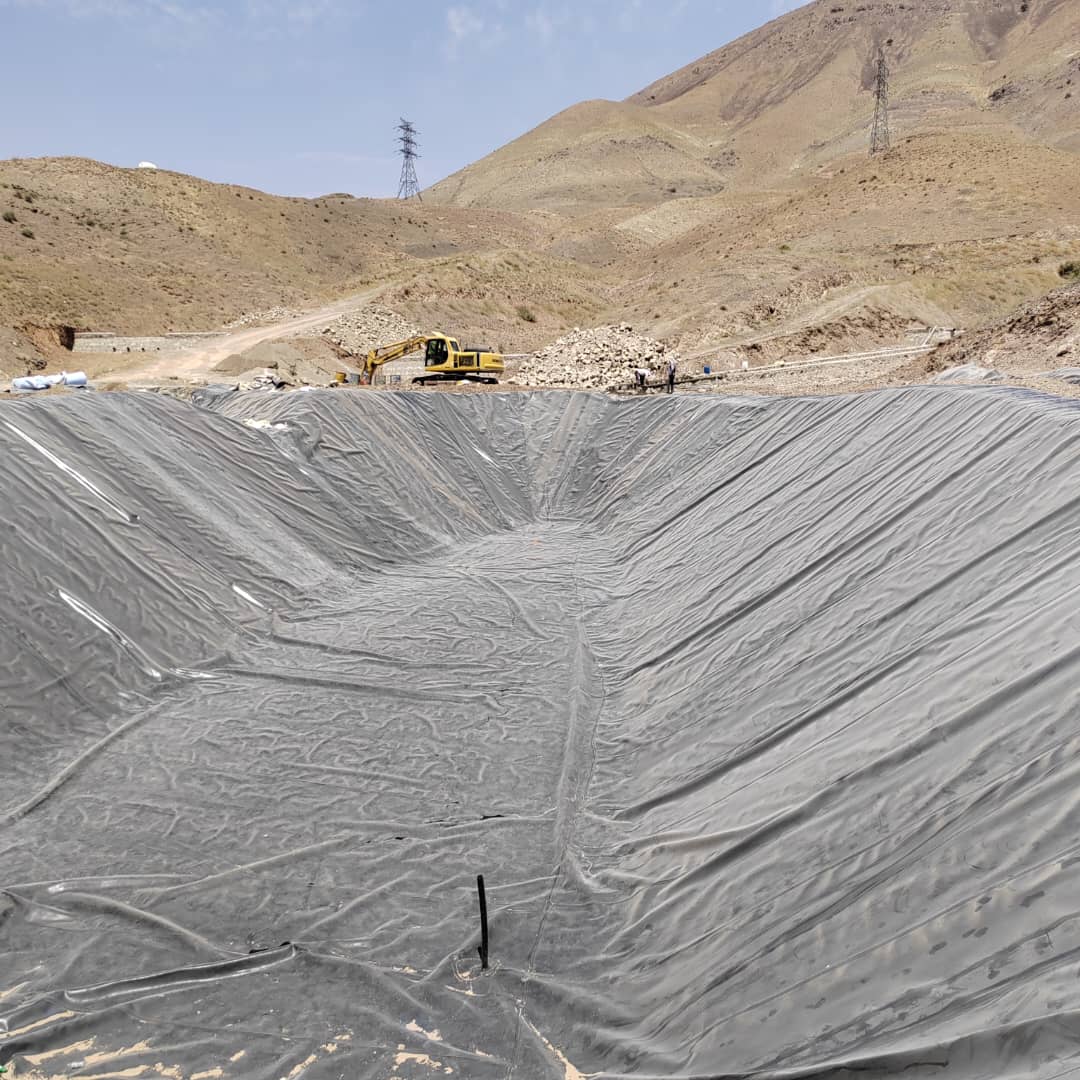
Plastic construction materials refer to various plastic-based products used in the construction industry for building and infrastructure projects. These materials offer a range of benefits such as durability, versatility, ease of installation, and resistance to environmental factors.
Here are some common plastic construction materials:
1. Pipes and Fittings: Plastic pipes, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride), PEX (cross-linked polyethylene), and HDPE (high-density polyethylene), are widely used for plumbing, drainage, irrigation, and other fluid transportation applications. Plastic fittings are used to connect pipes and create joints in plumbing systems.
2. Insulation Materials : Plastic foam insulation materials, such as expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), and polyurethane foam, are used to insulate walls, roofs, floors, and foundations. These materials provide thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and energy efficiency.
3. Roofing Materials : Plastic roofing materials, including PVC roofing membranes, polycarbonate panels, and acrylic sheets, are used for roofing applications such as flat roofs, skylights, and roofing overlays. These materials offer durability, UV resistance, and weatherproofing properties.
4. Siding and Cladding: Plastic siding materials, such as vinyl siding and fiber cement siding with plastic additives, are used to clad exterior walls of buildings. These materials offer durability, low maintenance, and resistance to rot, insects, and weathering.
5. Windows and Doors : Plastic windows and doors, made from materials such as PVC and fiberglass, are used in residential, commercial, and institutional buildings. These materials offer energy efficiency, sound insulation, and low maintenance compared to traditional materials like wood and metal.
6. Composite Materials: Plastic composite materials, such as wood-plastic composites (WPC) and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites, are used for decking, fencing, railings, and structural components. These materials combine the benefits of plastic with the strength and aesthetics of natural materials like wood and fiberglass.
7. Geosynthetic Materials : Plastic geosynthetic materials, such as geomembranes, geotextiles, and geogrids, are used in civil engineering and environmental applications for soil stabilization, erosion control, drainage, and containment of liquids and gases.
_1710693928.jpg)
Plastic construction materials offer advantages such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, ease of handling, and design flexibility. However, proper installation, maintenance, and disposal practices are essential to mitigate environmental impacts and ensure the longevity of plastic construction materials. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing sustainable plastic construction materials, including recycled plastics and biodegradable alternatives, to address environmental concerns associated with plastic waste.
Plastic packaging refers to the use of plastic materials to package, store, and protect products. Plastic packaging comes in various forms, including bottles, containers, bags, films, wraps, trays, and clamshells. It is widely used across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, personal care, household goods, and industrial products due to its versatility, durability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness.
_1710693899.jpg)
Plastic construction materials refer to various plastic-based products used in the construction industry for building and infrastructure projects. These materials offer a range of benefits such as durability, versatility, ease of installation, and resistance to environmental factors.
_1710693928.jpg)
FAQs
What is plastic known as?
Plastic products encompass a wide range of items made from synthetic polymers, also known as plastics.
Where is plastic used in construction?
Plastics are used in construction for various purposes, including pipes, fittings, insulation materials, roofing materials, flooring, window frames,
What is the purpose of plastic packaging?
Plastic packaging refers to the use of plastic materials to package, store, and protect products
What is the effect of plastic packaging on the environment?
Despite its benefits, plastic also poses environmental challenges, particularly related to plastic waste and pollution.
 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
 English
English
 Persian
Persian
 Russian
Russian
 Chinese
Chinese


 +7929688-88-14
+7929688-88-14
















.png)















